Local Injection of Fluid Gelatin Under Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Guidance for Treating Active Bleeding From the Inferior Epigastric Artery: A Case Report
- PMID: 40462389
- PMCID: PMC12147519
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.947297
Local Injection of Fluid Gelatin Under Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Guidance for Treating Active Bleeding From the Inferior Epigastric Artery: A Case Report
Abstract
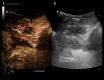
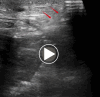
BACKGROUND Injury to the inferior epigastric artery is a major complication of abdominal puncture, and continuous active bleeding from this artery can lead to hemorrhagic shock. Several studies have reported the use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) to diagnose active bleeding in parenchymal organs. Fluid gelatin is a new hemostatic material that can be injected into the bleeding site by using a puncture needle under the precise guidance of CEUS, which enables the implementation of local minimally invasive and appropriate hemostatic treatment. Here, we report the case of a patient in whom CEUS was used to accurately locate the bleeding site before surgery and guide local injection of fluid gelatin with a puncture needle to successfully achieve nonsurgical treatment of hemostasis. CASE REPORT A 62-year-old man with post-hepatitis B cirrhosis underwent a successful liver transplant surgery. After surgery, abdominal puncture and drainage were performed because of a large amount of peritoneal effusion due to nephrotic syndrome. The drainage fluid was bright red bloody liquid. CEUS revealed many contrast agent microbubbles extravasating from the inferior epigastric artery into peritoneal effusion along the abdominal puncture tract. Surgical suturing and applying a compression bandage failed to achieve satisfactory results. After receiving the patient's consent, thrombin and hemostatic glue were injected locally under the guidance of CEUS. Finally, hemostasis was successfully achieved. CONCLUSIONS CEUS-guided injection of fluid gelatin is a safe and effective treatment method and could serve as an effective measure for nonsurgical treatment and postoperative supplementary treatment of active bleeding from the inferior epigastric artery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Epstein J, Arora A, Ellis H. Surface anatomy of the inferior epigastric artery in relation to laparoscopic injury. Clin Anat. 2004;17(5):400–8. - PubMed
-
- Härkki-Siren P, Sjöberg J, Kurki T. Major complications of laparoscopy: A follow-up Finnish study. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;94(1):94–98. - PubMed
-
- Wong C, Merkur H. Inferior epigastric artery: Surface anatomy, prevention and management of injury. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;56(2):137–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

