Cognitive Dysfunction in the Addictions (CDiA): protocol for a neuron-to-neighbourhood collaborative research program
- PMID: 40462873
- PMCID: PMC12131087
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1455968
Cognitive Dysfunction in the Addictions (CDiA): protocol for a neuron-to-neighbourhood collaborative research program
Abstract
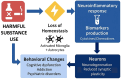
Substance use disorders (SUDs), including Alcohol Use Disorder, are pressing global public health problems. Executive functions (EFs) are prominently featured in mechanistic models of addiction. However, significant gaps remain in our understanding of EFs in SUDs, including the dimensional relationships of EFs to underlying neural circuits, molecular biomarkers, disorder heterogeneity, and functional ability. Transforming health outcomes for people with SUDs requires an integration of clinical, biomedical, preclinical, and health services research. Through such interdisciplinary research, we can develop policies and interventions that align with biopsychosocial models of addiction, addressing the complex cognitive concerns of people with SUDs in a more holistic and effective way. Here, we introduce the design and procedures underlying Cognitive Dysfunction in the Addictions (CDiA), an integrative research program, which aims to fill these knowledge gaps and facilitate research discoveries to enhance treatments for people living with SUDs. The CDiA Program comprises seven interdisciplinary projects that aim to evaluate the central thesis that EF has a crucial role in functional outcomes in SUDs. The projects draw on a diverse sample of adults aged 18-60 (target N=400) seeking treatment for SUD, who are followed over one year to identify specific EF domains most associated with improved functioning. Projects 1-3 investigate SUD symptoms, brain circuits, and blood biomarkers and their associations with key EF domains (inhibition, working memory, and set-shifting) and functional outcomes (disability, quality of life). Projects 4 and 5 evaluate interventions for SUDs and their impacts on EF: a clinical trial of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and a preclinical study of potential new pharmacological treatments in rodents. Project 6 links EF to healthcare utilization and is supplemented with a qualitative investigation of EF-related barriers to treatment engagement. Project 7 uses whole-person modeling to integrate the multi-modal data generated across projects, applying clustering and deep learning methods to identify patient subtypes and drive future cross-disciplinary initiatives. The CDiA Program will bring scientific domains together to uncover novel ways in which EFs are linked to SUD severity and functional recovery, and facilitate future discoveries to improve health outcomes in individuals living with SUDs.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol use disorder; cognition; executive function; preclinical; substance use disorder; translational.
Copyright © 2025 Nikolova, Ruocco, Felsky, Lange, Prevot, Vieira, Voineskos, Wardell, Blumberger, Clifford, Naik Dharavath, Gerretsen, Hassan, Hope, Irwin, Jennings, Le Foll, Melamed, Orson, Pangarov, Quigley, Russell, Shield, Sloan, Smoke, Tang, Valdes Cabrera, Wang, Wells, Wickramatunga, Sibille and Quilty.
Conflict of interest statement
DB received research support and in-kind equipment support for an investigator-initiated study from Brainsway Ltd. He was the site principal investigator for three sponsor-initiated studies for Brainsway Ltd. He also received in-kind equipment support from Magventure for two investigator-initiated studies. He received medication supplies for an investigator-initiated trial from Indivior. He is a scientific advisor for Sooma Medical. He is the Co-Chair of the Clinical Standards Committee of the Clinical TMS Society unpaid. TP and ES are listed as inventors on patents covering the use of molecules proposed to be tested in the described study. TP also acts as the Director of Preclinical Research and Development of DAMONA Pharmaceuticals, a spin-off company from CAMH aiming at leading the licensed technology to the clinical for reduction of cognitive deficits in brain disorders. ES acts as the CSO and Founder of DAMONA Pharmaceuticals. BF has obtained funding from Indivior for a clinical trial sponsored by Indivior. BF has in-kind donations of placebo edibles from Indivia. BF has obtained industry funding from Canopy Growth Corporation through research grants handled by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health and the University of Toronto. BF has participated in a session of a National Advisory Board Meeting Emerging Trends BUP-XR for Indiva Canada and is part of Steering Board for a clinical trial for Indiva. BF has been a consultant for Shinogi and ThirdBridge. BF got travel support to attend an event by Bioprojet. BF is supported by CAMH, Waypoint Centre for Mental Health Care, a clinician-scientist award from the department of Family and Community Medicine of the University of Toronto and a Chair in Addiction Psychiatry from the department of Psychiatry of University of Toronto. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Update of
-
Cognitive Dysfunction in the Addictions (CDiA): A Neuron to Neighbourhood Collaborative Research Program on Executive Dysfunction and Functional Outcomes in Outpatients Seeking Treatment for Addiction.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 28:2024.08.30.24312806. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.24312806. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Front Psychiatry. 2025 May 19;16:1455968. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1455968. PMID: 39252904 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Rehm J, Probst C, Falcón LL, Shield KD. Burden of Disease: The Epidemiological Aspects of Addiction. In: el-Guebaly N, Carrà G, Galanter M, Baldacchino AM, editors. Textbook of Addiction Treatment: International Perspectives. Springer International Publishing, Cham: (2021). p. 51–64.
-
- GBD Results . Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation . Available online at: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/ (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

