This is a preprint.
SARM1 is an essential component of neuronal Parthanatos
- PMID: 40463025
- PMCID: PMC12132571
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.14.654090
SARM1 is an essential component of neuronal Parthanatos
Abstract
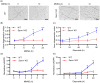
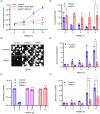
The NAD+ hydrolase SARM1 is the central executioner of pathological axon degeneration. SARM1 is allosterically activated by an increased NMN/NAD+ ratio resulting from depletion of NAD+ or accumulation of its precursor, NMN, typically due to loss of the labile NAD+ synthetase NMNAT2 following axon injury. Another NAD+ hydrolase, PARP1, is hyperactivated by DNA damage, triggering the Parthanatos cell death pathway. We demonstrate that multiple mechanistically-distinct DNA-damaging agents lead to SARM1 activation and axon degeneration following PARP1 activation. Remarkably, SARM1 is required for key steps downstream of PARP1 activation by DNA damage that are pathognomonic of Parthanatos, including mitochondrial depolarization, nuclear translocation of AIF (apoptosis-inducing factor), and cell death. Moreover, SARM1 mediates glutamate excitotoxicity, a clinically significant pathomechanism attributed to Parthanatos. The identification of SARM1 as an essential component of neuronal Parthanatos, a major contributor to cell death in neurodegenerative disease, greatly expands the potential clinical utility of SARM1 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests JM and AD are co-founders, scientific advisory board members, and shareholders of Disarm Therapeutics, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly and scientific advisory board members of Asha Therapeutics. The authors have no other competing conflicts or financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nicotinic acid mononucleotide is an allosteric SARM1 inhibitor promoting axonal protection.Exp Neurol. 2021 Nov;345:113842. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113842. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34403688 Free PMC article.
-
TAX1BP1 contributes to deoxypodophyllotoxin-induced glioma cell parthanatos via inducing nuclear translocation of AIF by activation of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Sep;44(9):1906-1919. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01091-w. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37186123 Free PMC article.
-
SARM1 is a metabolic sensor activated by an increased NMN/NAD+ ratio to trigger axon degeneration.Neuron. 2021 Apr 7;109(7):1118-1136.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.02.009. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 33657413 Free PMC article.
-
SARM1-Dependent Axon Degeneration: Nucleotide Signaling, Neurodegenerative Disorders, Toxicity, and Therapeutic Opportunities.Neuroscientist. 2024 Aug;30(4):473-492. doi: 10.1177/10738584231162508. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Neuroscientist. 2024. PMID: 37002660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemical biology of NAD+ regulation in axon degeneration.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Aug;69:102176. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102176. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35780654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Di Stefano M., Nascimento-Ferreira I., Orsomando G., Mori V., Gilley J., Brown R., Janeckova L., Vargas M.E., Worrell L.A., Loreto A., et al. (2015). A rise in NAD precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) after injury promotes axon degeneration. Cell Death Differ 22, 731–742. 10.1038/cdd.2014.164. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
