This is a preprint.
Serine palmitoyltransferase-mediated de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis is required for normal insulin production and glucose tolerance
- PMID: 40463068
- PMCID: PMC12132366
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.14.653935
Serine palmitoyltransferase-mediated de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis is required for normal insulin production and glucose tolerance
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: The importance for normal insulin secretion of ceramide synthesis is unclear. De novo ceramide synthesis requires serine palmitoyl transferase, SPT2, encoded by Sptl2.
Methods: We generated β-cell-selective Sptl2 null mice by crossing animals with floxed alleles to mice expressing Cre recombinase from the Ins1 locus. Metabolic phenotyping, transcriptomic, functional analyses and histology were performed using standard approaches.
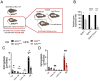
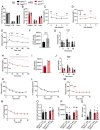
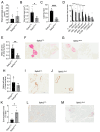
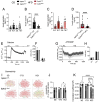
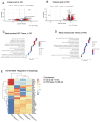
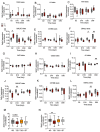
Results: Islets from Sptlc2 ΔInsl mice displayed marked alterations in ceramide and sphingomyelin levels: ceramide content: p=0.016 and p=0.109; sphingomyelin content: p=0.016 and p=0.004 in Sptlc2 ΔInsl vs Sptlc2 CTL mice under regular and high fat diet, respectively, despite compensatory increases in the expression of enzymes in the salvage and sphingomyelinase pathways. Correspondingly, profound abnormalities were observed in glucose-regulated insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in vivo, both on a regular chow and high fat diet. These changes were associated with a drastic (~80%) lowering in β-cell numbers, and a more minor increase in delta cell numbers. They were also preserved in animals maintained on a ketogenic diet, consistent with a cell autonomous effect on the β-cell. Despite normal glucose-regulated intracellular calcium dynamics and insulin secretion, marked transcriptomic changes were observed in Sptlc2 ΔInsl mouse islets, with affected GO terms including lysosome organisation and regulation of autophagy. Consistent with roles for compromised SPT2 function in diseased β-cells, Sptl2 expression in Balbc and DBA2J mouse islets was lowered by a high fat-diet. Moreover, SPTLC2 mRNA tended to be lower, and SPTLC1 mRNA was significantly decreased, in islets from human subjects with type 2 diabetes versus normoglycemic individuals.
Conclusions: Preserved de novo ceramide synthesis is required to maintain normal β-cell mass and thus insulin secretion in mice. Therapeutic approaches which seek to target this process systemically using pharmacological SPT2 inhibitors should thus be treated with caution.
Keywords: Beta cell mass; ceramides; diabetes; sphingomyelin.
Conflict of interest statement
GR has received grant funding from, and is a consultant for, Sun Pharmaceuticals Inc. Other authors have no relevant financial disclosures. We thank the animal core facility Buffon of the Université Paris Cité.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
