This is a preprint.
A GATA factor radiation in Caenorhabditis rewired the endoderm specification network
- PMID: 40463085
- PMCID: PMC12132343
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.05.20.492851
A GATA factor radiation in Caenorhabditis rewired the endoderm specification network
Abstract
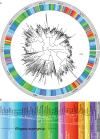
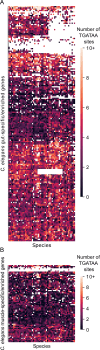
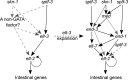
Although similar developmental regulatory networks can produce diverse phenotypes, different networks can also produce the same phenotype. In theory, as long as development can produce an acceptable end phenotype, the details of the process could be shielded from selection, leading to the possibility of developmental system drift, where the developmental mechanisms underlying a stable phenotype continue to evolve. Many examples exist of divergent developmental genetics underlying conserved traits. However, studies that elucidate how these differences arose and how other features of development accommodated them are rarer. In Caenorhabditis elegans, six transcription factors that bind motifs with a GATA core sequence (GATA factors) comprise the zygotic part of the endoderm specification network. Here we show that the core of this network - five of the genes - originated within the genus during a brief but explosive radiation of this gene family and that at least three of them evolved from a single ancestral gene with at least two different spatio-temporal expression patterns. Based on analyses of their evolutionary history, gene structure, expression, and sequence, we explain how these GATA factors were integrated into this network. Our results show how gene duplication fueled the developmental system drift of the endoderm network in a phylogenetically brief period in developmentally canalized nematodes.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Baugh LR, Hill AA, Slonim DK, Brown EL, Hunter CP. 2003. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development 130:889–900. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
