This is a preprint.
Oncolytic HSV-IL27 expression improves CD8 T cell function and therapeutic activity in syngeneic glioma models
- PMID: 40463203
- PMCID: PMC12132539
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.12.653429
Oncolytic HSV-IL27 expression improves CD8 T cell function and therapeutic activity in syngeneic glioma models
Update in
-
Oncolytic HSV-IL27 expression improves CD8 T cell function and therapeutic activity in syngeneic glioma models.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jul 7;13(7):e012227. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-012227. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40623717 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Malignant gliomas (MG) are the most common primary brain malignancies and are considered universally fatal. Oncolytic HSVs (oHSV) are promising immunotherapeutics capable of selectively lysing cancer cells, eliciting anti-tumor immunity, and providing local delivery of immune-activating transgenes. IL-27 is a pleiotropic cytokine capable of enhancing tumor-reactive cytotoxic T cell (CTL) function while also possessing neuroprotective properties. We hypothesized that IL-27 expression by oHSV would enhance CTL function and improve anti-glioma therapeutic activity.
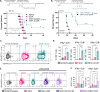
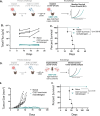
Methods: We developed an oncolytic herpes simplex virus (oHSV) that expresses IL-27 (C027). The anti-glioma efficacy of C027 was tested in three syngeneic orthotopic glioma models derived from both chemical (CT-2A) and genetic (SB28, KR158) glioma lines. Spectral flow cytometry was used to assess immunophenotypic and functional changes in the tumor infiltrates and systemically. To further investigate the C027-related CTL activity, we employed in vivo cell specific depletion and IL-27 blockade alongside in vitro T cell stimulation assays. Local and systemic antitumor memory was evaluated by both orthotopic and flank tumor rechallenge of C027-treated long-term survivors.
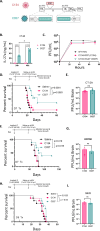
Results: C027 significantly prolonged survival in syngeneic orthotopic glioma models derived from both chemical (CT-2A) and genetic (KR158, SB28) glioma lines. In the CT-2A model, IL-27-expressing oHSV treatment was associated with increased intratumoral multifunctional effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and functional T cell populations systemically. Mechanistically, both CD8 T cells and IL-27 were required for the C027 survival benefit in vivo and IL-27 enhanced CTL function in vitro. C027-treated mice that survived their initial tumors had local and systemic anti-glioma memory rejecting tumors on rechallenge.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that IL-27 expression by oHSV significantly improves anti-glioma therapeutic efficacy, enhances CTL effector function, and induces durable immune memory. Thus, IL-27-oHSV may provide a promising therapeutic approach for malignant gliomas.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests KAC receives licensure payments from Mustang Bio for the C134 virus, but there are no relevant financial conflicts for the technology addressed in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–66. - PubMed
-
- Noch EK, Ramakrishna R, Magge R. Challenges in the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Multisystem Mechanisms of Therapeutic Resistance. World Neurosurg. 2018;116:505–17. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
