This is a preprint.
Embryonic Stem Cell-Specific Responses to DNA Replication Stress
- PMID: 40463205
- PMCID: PMC12132374
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.16.654332
Embryonic Stem Cell-Specific Responses to DNA Replication Stress
Abstract
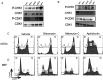
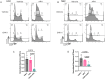
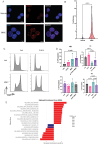
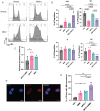
Genome maintenance is of the utmost importance in stem cells, as mutations can be propagated and cause defects in derivative tissues. Many stem cell types display low mutation rates, with embryonic stem cells (ESCs) being a notable example. The bases for this property are unclear but may be achieved by optimization of various processes including high-fidelity DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoint controls, and hypersensitivity to genotoxic insults that trigger cell death. Here, we investigate the mechanisms underlying the unique responses of mouse ESCs (mESCs) to replication stress (RS) using an array of small molecule inhibitors and genotoxins. We find that whereas mESCs survive under acute RS in an ATR- and CHK1-dependent manner similar to somatic cells, they lack a strong G2/M checkpoint and fail to repair DNA crosslinks in the absence of ATR signaling. Despite the lack of a strong G2/M checkpoint, mESCs maintain a spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). We posit that mESCs preferentially repair DNA crosslinks in S phase via homology-directed mechanisms, and cells that fail to complete repair before mitosis undergo mitotic catastrophe and cell death. These findings shed light on mutation avoidance mechanisms in ESCs that may extend to other stem cell types.
Figures

References
-
- Coronado D., Godet M., Bourillot P.-Y., Tapponnier Y., Bernat A., Petit M., Afanassieff M., Markossian S., Malashicheva A., Iacone R., et al. (2013). A short G1 phase is an intrinsic determinant of naïve embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Stem Cell Res. 10, 118–131. 10.1016/j.scr.2012.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neganova I., Tilgner K., Buskin A., Paraskevopoulou I., Atkinson S.P., Peberdy D., Passos J.F., and Lako M. (2014). CDK1 plays an important role in the maintenance of pluripotency and genomic stability in human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1508. 10.1038/cddis.2014.464. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
