Fc-effector functional antibody assays for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern
- PMID: 40463385
- PMCID: PMC12130042
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571835
Fc-effector functional antibody assays for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern
Abstract
Background: The Fc regions of antibodies mediate important effector cell functions such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), antibody-dependent neutrophil phagocytosis (ADNP), and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). These functions enhance immune defense and infected cell clearance. This study evaluated the effect COVID-19 XBB.1.5 booster vaccination on Fc-effector antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2.
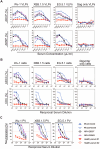
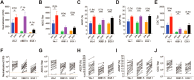
Methods: We developed four assays to evaluate the Fc-effector functions of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. ADCC and CDC assays utilized stably transfected luciferase-based target cell lines expressing SARS-CoV-2 spike variants (Ancestral, Wu-1 Omicron XBB.1.5, and EG.5) to measure antibody-mediated lysis by effector cells. ADCP and ADNP were assessed by flow cytometry to measure phagocytosis of fluorescently labeled virus-like particles that display SARS-CoV-2 variant spike proteins. Serum samples from 20 healthy adult volunteers pre- and post-monovalent XBB.1.5 COVID-19 vaccine were analyzed for pseudovirus neutralizing and Fc-effector antibodies.
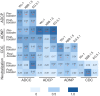
Results: Prior to administration of the COVID-19 XBB.1.5 booster vaccination, cross-neutralizing antibodies against XBB.1.5 and EG.5 variants were minimally detectable, while cross-functional Fc-effector antibodies were present at higher baseline levels. The COVID-19 XBB.1.5 booster vaccination significantly boosted both neutralizing and Fc-effector antibodies in magnitude and breadth. The greatest increase in neutralizing antibodies was against the XBB.1.5 strain, while Fc-effector functional antibodies had similar fold-increases in antibody titers against the breadth of SARS-CoV-2 variants tested. Neutralizing and Fc-effector antibodies were most highly correlated at baseline (prior to booster vaccination) but were less correlated post-vaccination, consistent with differential boosting of neutralizing vs Fc-effector antibodies by the monovalent vaccine.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 XBB.1.5 booster vaccination significantly improved the magnitude, breadth, and quality of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2. Combining Fc-mediated functional and neutralizing antibody assays provides a more comprehensive model for understanding vaccine-induced immunity and optimizing vaccination strategies.
Keywords: ADCC; ADCP; ADNP; complement deposition; cytotoxicity; non-neutralizing antibodies; phagocytosis.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Li, Ciric, Gibson, Anderson and Rostad.
Conflict of interest statement
Author LA has done paid consultancies on RSV vaccines for AstraZeneca, Bavarian Nordic, GSK, and Janssen and on influenza virus vaccines for Pfizer. His laboratory is currently receiving funding through Emory University from Pfizer for RSV surveillance and maternal infant studies and from Advac, Sciogen, and Vernagen for RSV vaccine-related studies. Author LA is co-inventor on several Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC or Emory patents or patent filings on the RSV G protein and its CX3C chemokine motif relative to immune therapy and vaccine development and a patent filing for use of RSV platform VLPs, virus-like particles, with the F and G proteins for vaccines. Author CR’s institution has received funds to conduct clinical research unrelated to this manuscript from Janssen, Merck, Moderna, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Pasteur. Authors XC, LA, and CR are co-inventors of Fc effector assays subject to evaluation in this manuscript. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 BA.4/5 infection triggers more cross-reactive FcγRIIIa signaling and neutralization than BA.1, in the context of hybrid immunity.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0067824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00678-24. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38953380 Free PMC article.
-
XBB.1.5 monovalent vaccine induces lasting cross-reactive responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants such as HV.1 and JN.1, as well as SARS-CoV-1, but elicits limited XBB.1.5 specific antibodies.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0360724. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03607-24. Epub 2025 Mar 5. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40042313 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative immunogenicity of monovalent and bivalent adenovirus vaccines carrying spikes of early and late SARS-CoV-2 variants.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2387447. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2387447. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 39082740 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Fc-effector functions against SARS-CoV-2.Trends Microbiol. 2024 Aug;32(8):756-768. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Trends Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38365562 Review.
-
More antibodies are not always better: Fc effector functions play a critical role in SARS-CoV-2 infection and protection.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2025;213:413-447. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2025.02.001. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40246351 Review.
References
-
- Beaudoin-Bussieres G, Chen Y, Ullah I, Prevost J, Tolbert WD, Symmes K, et al. . A Fc-enhanced NTD-binding non-neutralizing antibody delays virus spread and synergizes with a nAb to protect mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. (2022) 38:110368. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gorman MJ, Patel N, Guebre-Xabier M, Zhu A, Atyeo C, Pullen KM, et al. . Collaboration between the Fab and Fc contribute to maximal protection against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates following NVX-CoV2373 subunit vaccine with Matrix-M vaccination. bioRxiv. (2021). doi: 10.1101/2021.02.05.429759 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

