The neurobiology of plant-based therapeutics in women's reproductive health: mechanisms, efficacy, and clinical translation
- PMID: 40463464
- PMCID: PMC12129779
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1591534
The neurobiology of plant-based therapeutics in women's reproductive health: mechanisms, efficacy, and clinical translation
Abstract
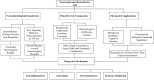
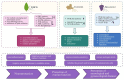
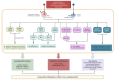
This review examines the neurobiological mechanisms by which plant-derived compounds influence women's reproductive health through the neuroendocrine-reproductive axis. Gynecological disorders frequently present with neurological manifestations, including cognitive decline in perimenopause, anxiety and depression in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and central sensitization in endometriosis. Bioactive compounds from medicinal plants, including polyphenols and phytoestrogens, demonstrate therapeutic potential through their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuromodulatory properties. These multi-target compounds offer advantages over conventional single-target therapies by simultaneously regulating multiple physiological processes. The review explores applications in specific gynecological conditions and discusses the development of dietary supplements and functional foods incorporating these plant-derived ingredients. The growing market for these products presents opportunities for innovative formulations with enhanced bioavailability and personalized approaches. Future research directions include integrating neuroimaging with herbal research, improving clinical translation, and establishing regulatory frameworks for the global application of these plant-derived interventions to enhance female neuroendocrine-reproductive health.
Keywords: functional foods; neuroendocrine-reproductive axis; phytoestrogens; plant-derived compounds; women's health.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Bin, Zhou, Zeng, Wu, Luo, Liu and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hantsoo L, Jagodnik KM, Novick AM, Baweja R, di Scalea TL, Ozerdem A, et al. . The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in depression across the female reproductive lifecycle: current knowledge and future directions. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1295261. 10.3389/fendo.2023.1295261 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

