Lung Transplant Outcomes in Patients With Preoperative Catheterization Indicating Group 2 Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 40463492
- PMCID: PMC12130283
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.70107
Lung Transplant Outcomes in Patients With Preoperative Catheterization Indicating Group 2 Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
Lung transplantation (LT) is a well-established therapeutic option for patients with advanced chronic respiratory diseases. This study aims to assess the prevalence and clinical impact of Group 2 pulmonary hypertension (PHg2) in LT recipients, comparing it with Group 3 pulmonary hypertension (PHg3). This retrospective cohort study analyzed LT recipients from 2015 to 2024 at a single center. Patients were categorized into three groups based on hemodynamic measurements: no PH, PHg2, and PHg3. Hemodynamic data were acquired via right heart catheterization. Perioperative complications, including primary graft dysfunction (PGD), and long-term survival were compared across the groups. Of the 412 LT recipients, 40 (10.9%) were diagnosed with PHg2, while 62.5% had PHg3. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences in perioperative outcomes, including the incidence of PGD, between patients with PHg2 and those with PHg3. Additionally, there were no differences in long-term survival between the groups. Within the PHg2 subgroup, patients with isolated PHg2 and those with combined PHg2 exhibited similar post-transplant outcomes. PHg2 is identified in a notable fraction of LT recipients, yet it does not appear to adversely affect perioperative complications or long-term survival when compared to PHg3 or patients without PH. These findings suggest that PHg2, despite its prevalence, does not significantly alter transplant outcomes. Future multicenter studies are needed to further explore the impact of subtle left ventricular dysfunction on LT results.
Keywords: lung transplantation; primary graft dysfunction; pulmonary hypertension.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pulmonary Circulation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
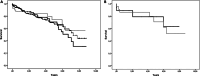
References
-
- Weill D., Benden C., Corris P. A., et al., “A Consensus Document for the Selection of Lung Transplant Candidates: 2014—An Update From the Pulmonary Transplantation Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation,” Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 34, no. 1 (January 2015): 1–15, 10.1016/j.healun.2014.06.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leard L. E., Holm A. M., Valapour M., et al., “Consensus Document for the Selection of Lung Transplant Candidates: An Update From the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation,” Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 40, no. 11 (November 2021): 1349–1379, 10.1016/j.healun.2021.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mora‐Cuesta V. M., Martínez‐Meñaca A., Iturbe‐Fernández D., et al., “Impact of the New Definition of Pulmonary Hypertension on the Prevalence of Primary Graft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients,” Heart, Lung and Circulation 33, no. 4 (April 2024): 524–532, 10.1016/j.hlc.2023.12.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diamond J. M., Arcasoy S., Kennedy C. C., et al., “Report of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction, Part II: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Outcomes—A 2016 Consensus Group Statement of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation,” Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 36, no. 10 (October 2017): 1104–1113, 10.1016/j.healun.2017.07.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

