Natural Killer Cell Immune Checkpoints and Their Therapeutic Targeting in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 40463500
- PMCID: PMC12131497
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0723
Natural Killer Cell Immune Checkpoints and Their Therapeutic Targeting in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
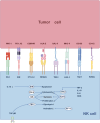
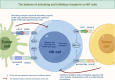
Natural killer (NK) cells, serving as pivotal mediators of innate immunity, play an important role in antitumor immunity. Immune checkpoint can be expressed on the surface of NK cells and meticulously regulates their activation states and effector functions through complex signaling networks. In recent years, tumor immunotherapy strategies focusing on NK cell immune checkpoints have demonstrated remarkable advancements. This review systematically elucidates the expression profiles, signaling pathways, and the immune checkpoint molecule regulatory mechanisms localized on the NK cell membrane (e.g., NKG2A, KIRs, and TIGIT) or intracellularly (e.g., BIM, Cbl-b, and EZH2) during tumor immune evasion. Particular attention is devoted to dissecting the regulatory mechanisms through which these immune checkpoint molecules influence NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, cytokine secretion, proliferative capacity, and tunable modulation of NK cell immune checkpoint expression by diverse factors within the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, this review comprehensively summarizes preclinical advancements in NK cell immune checkpoint blockade strategies, including single checkpoint blockade, combinatorial checkpoint approaches, and their integration with conventional therapeutic modalities. Additionally, emerging therapeutic advancements, such as gene-editing technologies and chimeric antigen receptor-NK (CAR-NK) cell therapy, are evaluated for their prospective applications in immunotherapy based on NK cells. By thoroughly elucidating the molecular regulatory networks underlying NK cell immune checkpoints and their mechanisms of action within the complex tumor microenvironment, this review aims to provide critical theoretical insights and translational foundations to foster the development of innovative tumor immunotherapy strategies, improvement of combination therapies, and realization of personalized precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Anqi Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Saadh MJ, Rasulova I, Khalil M, Farahim F, Sârbu I, Ciongradi CI, et al. . Natural killer cell-mediated immune surveillance in cancer: Role of tumor microenvironment. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;254:155120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

