Validating a Multidimensional Perspective of the Relationship Between Workplace Bullying, Professional Quality of Life, and Turnover Intention of Chinese Novice Nurses
- PMID: 40463513
- PMCID: PMC12133365
- DOI: 10.1155/jonm/6653143
Validating a Multidimensional Perspective of the Relationship Between Workplace Bullying, Professional Quality of Life, and Turnover Intention of Chinese Novice Nurses
Abstract
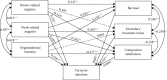
Background: The global shortage of nurses is a pressing social issue, and the high mobility of the nursing profession further exacerbates this challenge. Novice nurses' experiences of workplace bullying significantly increase their risk of leaving the profession. Therefore, exploring the mechanisms by which workplace bullying affects novice nurses' turnover intention is important for alleviating the nursing shortage and maintaining the stability of the nursing workforce. Method: This cross-sectional study of 832 novice nurses in northeastern China self-reports assessed workplace bullying, professional quality of life, and turnover intention-related status. The structural equation model was developed to analyze how workplace bullying (including person-related negative, work-related negative, and organizational injustice) affects turnover intention through the mediating role of the professional quality of life (compassion satisfaction, burnout, and secondary traumatic stress). Result: The results indicated that workplace bullying was significantly associated with novice nurses' turnover intention. Person-related negativity, work-related negative, and organizational injustice can influence turnover intentions by decreasing company satisfaction and increasing burnout; furthermore, work-related negativity can increase turnover intention by exacerbating secondary traumatic stress. Conclusion: This study provides new perspectives for understanding novice nurses' psychological reactions and career decisions in a workplace bullying environment and provides empirical support for nursing management practices. The findings highlight the importance of effective intervention strategies to improve the stability of the nursing team, optimize the quality of patient care, and reduce nurse turnover.
Keywords: novice nurses; professional quality of life; turnover intention; workplace bullying.
Copyright © 2025 Simeng Dong et al. Journal of Nursing Management published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Framework Guidelines for Addressing Workplace Violence in the Health Sector . World Health Organization; 2002.
-
- Einarsen S., Hoel H., Notelaers G. Measuring Exposure to Bullying and Harassment at Work: Validity, Factor Structure and Psychometric Properties of the Negative Acts Questionnaire-Revised. Work & Stress . 2009;23(1):24–44. doi: 10.1080/02678370902815673. - DOI
-
- Hodgins M., McNamara P. M. An Enlightened Environment? Workplace Bullying and Incivility in Irish Higher Education. Sage Open . 2019;9(4) doi: 10.1177/2158244019894278. - DOI
-
- Busby L., Patrick L., Gaudine A. Upwards Workplace Bullying: A Literature Review. Sage Open . 2022;12(1) doi: 10.1177/21582440221085008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical