This is a preprint.
Association of [18F]Flortaucipir-PET and plasma p-tau217 with tau neuropathology in AD and other neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 40463541
- PMCID: PMC12132148
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.14.25326954
Association of [18F]Flortaucipir-PET and plasma p-tau217 with tau neuropathology in AD and other neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
Background and objectives: Evaluating tau biomarkers in patients with available autopsy data is critical for validating their sensitivity and specificity to detect Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic changes (ADNC). We examined the association between tau-PET (using [18F]Flortaucipir), plasma ptau-217, and measures of AD neuropathology in a group of clinically-impaired participants from a tertiary dementia center, including patients with AD and FTLD.
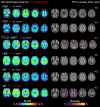
Methods: We analyzed Flortaucipir-PET (80-100 minutes post-injection acquisition, normalized to inferior cerebellar cortex) from 73 patients with a clinical diagnosis of various neurodegenerative diseases who underwent autopsy at the Neurodegenerative Disease Brain Bank (median [IQR] age: 67 [59, 73] years, 60% male, median [IQR] PET-to-autopsy duration: 3.9 years, [2.1, 5.1]). Standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) were extracted from the entorhinal cortex (an early tau region) and the temporal meta-ROI (a widely used AD signature region). A semi-quantitative rating of AD NFT burden in cortical areas was available for 56 participants. Plasma p-tau217 was quantified with Simoa (Janssen®) in 56 participants (median [IQR] PET-to-plasma duration: 1.7 months [0.5, 4.1]).
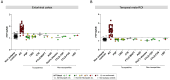
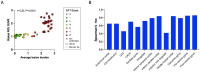
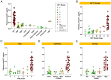
Results: Our cohort included patients with a primary pathological diagnosis of AD (n=39), FTLD (tauopathies n=28, non-tauopathies n=4), and Lewy body dementia (n=2). Flortaucipir SUVRs were elevated in patients with a neuropathological diagnosis of AD compared with non-AD patients. Consistently elevated PET signal was detected in both the entorhinal cortex and temporal meta-ROI of patients with neurofibrillary tangle (NFT) at Braak stage VI and with high ADNC levels. No elevation of Flortaucipir SUVRs was observed at intermediate levels of ADNC. The burden of AD NFTs was correlated with local Flortaucipir SUVRs across cortical brain regions. Plasma p-tau217 concentrations were increased in patients at Braak stage V and VI and strongly correlated with Flortaucipir SUVRs across ROIs (r's≥0.75), driven by Braak V-VI cases. Flortaucipir SUVRs and plasma p-tau217 concentrations identified high Braak stages (V-VI) and high/intermediate ADNC levels with similarly high performance (area under the curve≥ 0.90).
Discussion: Flortaucipir-PET and plasma p-tau217 both displayed strong specificity for primary AD neuropathological diagnosis but lacked sensitivity to detect early AD-related tau co-pathology in patients with a non-AD diagnosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; frontotemporal lobar degeneration; neurofibrillary tangle; neuropathology; plasma p-tau; positron emission tomography; tau.
Figures


References
-
- Avid Pharmaceuticals. Tauvid [Package Insert]. Eli Lily and Company; 2024. https://pi.lilly.com/us/tauvid-uspi.pdf
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
