This is a preprint.
Cortical connectivity predicts cognition across time in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40463555
- PMCID: PMC12132129
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.13.25327462
Cortical connectivity predicts cognition across time in Parkinson's disease
Update in
-
Cortical connectivity is associated with cognition across time in Parkinson's disease.Neuroimage Rep. 2025 Nov 12;5(4):100299. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2025.100299. eCollection 2025 Dec. Neuroimage Rep. 2025. PMID: 41322670 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Cognitive symptoms are common in Parkinson's disease (PD), yet the underlying brain mechanisms remain poorly understood. To address this gap, we investigated the relationship between functional connectivity and cognition at multiple time points using longitudinal functional MRI (fMRI) and cognitive assessments from the Parkinson's Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI). We calculated resting-state functional connectivity within and between three key cortical brain networks that have been linked with cognitive function in PD: the frontoparietal network (FPN); the salience network (SAL); and the default mode network (DMN). Cognitive function was assessed with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Linear mixed-effects modeling revealed that decreased FPN-DMN functional connectivity is associated with lower MoCA scores over time. This finding suggests that cortical connectivity is associated with and may contribute to the progression of cognitive symptoms in PD. Our findings advance knowledge about cognitive changes in PD and emphasize the importance of functional brain network architecture.
Figures
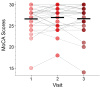
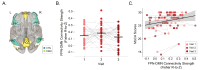
References
-
- Amboni M., Tessitore A., Esposito F., Santangelo G., Picillo M., Vitale C., Giordano A., Erro R., de Micco R., Corbo D., Tedeschi G., & Barone P. (2015). Resting-state functional connectivity associated with mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurology, 262(2), 425–434. 10.1007/s00415-014-7591-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aracil-Bolaños I., Sampedro F., Marín-Lahoz J., Horta-Barba A., Martínez-Horta S., Botí M., Pérez-Pérez J., Bejr-Kasem H., Pascual-Sedano B., Campolongo A., Izquierdo C., Gironell A., Gómez-Ansón B., Kulisevsky J., & Pagonabarraga J. (2019). A divergent breakdown of neurocognitive networks in Parkinson’s Disease mild cognitive impairment. Human Brain Mapping, 40(11), 3233–3242. 10.1002/hbm.24593 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., & Walker S. (2015). Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
