This is a preprint.
Moving beyond risk ratios in sibling analysis: estimating clinically useful measures from family-based analysis
- PMID: 40463571
- PMCID: PMC12132141
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.16.25327702
Moving beyond risk ratios in sibling analysis: estimating clinically useful measures from family-based analysis
Abstract
Objective: Findings from family-based analyses, such as sibling comparisons, are often reported using only odds ratios or hazard ratios. We demonstrate how this can be improved upon by applying the marginalized between-within framework.
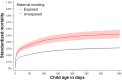
Study design and setting: We provide an overview of sibling comparison methods and the marginalized between-within framework, which enables estimation of absolute risks and clinically relevant metrics while accounting for shared familial confounding. We illustrate the approach using Swedish registry data to examine the association between maternal smoking and infant mortality, estimating absolute risk differences, average treatment effects, attributable fractions, and numbers needed to harm (or treat).
Results: The marginalized between-within model decomposes effects into within- and between-family components while applying a global baseline across all families. Although it typically yields similar relative estimates to conditional logistic or stratified Cox regression, the model's specification of a baseline enables the estimation of absolute measures. In the applied example, absolute measures provided more interpretable and policy-relevant insights than relative estimates alone. Code for implementation in Stata and R is provided.
Conclusion: The marginalized between-within framework may strengthen the interpretability of family-based analysis by enabling absolute and policy-relevant estimates for both binary and time-to-event outcomes, moving beyond the limitations of solely relying on relative effect measures.
Keywords: Absolute measures; Family-based analysis; Marginalized between-within models; Maternal Smoking; Sibling analysis; Within-family analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Sjölander A, Frisell T, Öberg S. Sibling Comparison Studies. Annual Review of Statistics and Its Application. 2022;9(1):71–94.
-
- Lambert PC, Wilkes SR, Crowther MJ. Flexible parametric modelling of the cause-specific cumulative incidence function. Stat Med. 2017;36(9):1429–1446. - PubMed
-
- Sjölander A. Estimation of marginal causal effects in the presence of confounding by cluster. Biostatistics. 2019;22(3):598–612. - PubMed
-
- Dahlqwist E, Pawitan Y, Sjolander A. Regression standardization and attributable fraction estimation with between-within frailty models for clustered survival data. Stat Methods Med Res. 2019;28(2):462–485. - PubMed
-
- Zhan Y, Liu XR, Reynolds CA, Pedersen NL, Hagg S, Clements MS. Leukocyte Telomere Length and All-Cause Mortality: A Between-Within Twin Study With Time-Dependent Effects Using Generalized Survival Models. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(10):2186–2191. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources