Complex Infective Endocarditis: Uncommon Presentations and Their Multisystem Complications - A Case Series
- PMID: 40463764
- PMCID: PMC12129267
- DOI: 10.4103/jcecho.jcecho_77_24
Complex Infective Endocarditis: Uncommon Presentations and Their Multisystem Complications - A Case Series
Abstract
Infective endocarditis (IE) is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by infection of the heart valves or endocardial surface, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. This case series explores four unusual presentations of IE, highlighting the diverse etiologies and complex multisystem complications that can arise from this condition. The clinical manifestations of IE can vary widely, ranging from systemic embolization to acute heart failure, reflecting the varied spectrum of pathogens involved and the patient's underlying health status. Key risk factors include preexisting valvular heart disease, intracardiac devices, intravenous drug use, and immunocompromised states. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management, with echocardiography serving as the gold standard imaging modality and playing a key role as the first-line tool. Both transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography are invaluable in identifying vegetations, evaluating valve function, and detecting potential complications such as abscesses, valve perforation, and intracardiac fistulas. The high sensitivity and specificity of echocardiography allow for early detection, even in cases with subtle or atypical presentations, ensuring that timely medical or surgical interventions are initiated. In addition, echocardiography is essential in monitoring treatment response, guiding clinical decisions, and determining the need for surgical valve replacement when severe damage or persistent infection is evident. This series emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, which may include both medical and surgical interventions, tailored to the patient's specific clinical scenario. A heightened awareness of atypical presentations and the need for timely intervention are critical for improving patient outcomes, particularly in high-risk populations.
Keywords: Case series; echocardiography; embolization; infective endocarditis; multisystem complications.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Cardiovascular Echography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
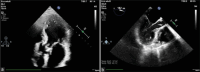
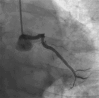
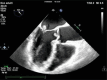
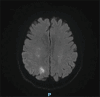
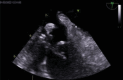
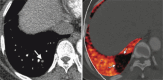
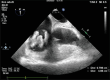
References
-
- Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, Fowler VG, Jr., Tleyjeh IM, Rybak MJ, et al. Infective endocarditis in adults: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;132:1435–86. - PubMed
-
- Zeng X, Liang Y, Wang H, Chen J, Xu Y, Ou Q, et al. Detection of pathogens from venous or arterial blood of patients with left-sided infective endocarditis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A prospective study. Clin Chim Acta. 2024;552:117698. - PubMed
-
- Vincent LL, Otto CM. Infective endocarditis: Update on epidemiology, outcomes, and management. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018;20:86. - PubMed
-
- Wang A, Gaca JG, Chu VH. Management considerations in infective endocarditis: A review. JAMA. 2018;320:72–83. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
