Traditional Chinese Medicine targeting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic strategy for renal fibrosis
- PMID: 40463902
- PMCID: PMC12130906
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1513329
Traditional Chinese Medicine targeting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic strategy for renal fibrosis
Abstract
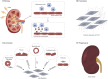
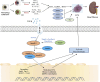
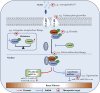
Renal fibrosis (RF) is an inevitable outcome of nearly all progressive chronic kidney diseases (CKD). However, effective therapies that can halt or reverse the development of RF and CKD progression remain limited. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a unique therapeutic approach, demonstrating significant anti-fibrotic potential through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pharmacological properties. However, comprehensive reviews focusing on the role of TCM in targeting signaling pathways associated with RF are still scarce. In this review, the literature was screened according to the clarity of the relevance of TCM, including the types and mechanisms of TCM. We summarize the pivotal role of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in RF and provide an overview of single Chinese botanical drug, their active ingredients, and TCM compounds that ameliorate RF by modulating this pathway, aiming to establish a solid foundation for future basic and clinical research in the field of RF. While TCM holds unique advantages in treating RF, its limitations need to be addressed through scientific research and technological innovation. Future studies will focus on elucidating mechanisms, improving quality control, validating clinical efficacy, and fostering international collaboration to promote the scientific and global application of TCM in modern medicine.
Keywords: Chinese herbal compounds; TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway; Traditional Chinese Medicine; renal fibrosis; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2025 Jiao, Zhang, Chen and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

