Status and trends in transcranial magnetic stimulation research: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40463940
- PMCID: PMC12129770
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1593987
Status and trends in transcranial magnetic stimulation research: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), as a rapidly advancing non-invasive brain stimulation technique, has demonstrated reliable therapeutic efficacy and significant potential in brain function assessment and research. However, comprehensive bibliometric analyses of the overall TMS field remain limited. Therefore, this study conducts a systematic analysis of TMS-related literature from 2004 to 2023, aiming to facilitate further advancements in TMS research and development.
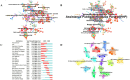
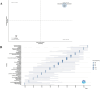
Methods: We retrieved TMS-related literature from 2004 to 2023 in the Web of Science Core Collection. Using CiteSpace and R language, we constructed network visualizations to illustrate annual publication outputs and journal distributions, demonstrate co-occurrence and collaboration patterns among authors, countries, and institutions, and establish keyword co-occurrence and reference co-citation analyses.
Results: Our analysis incorporated 6,278 TMS-related articles. Despite fluctuations, the publication output demonstrated an overall upward trend over the 20-year period. Daskalakis Z.J. emerged as the most prolific author, while the United States and Harvard University were identified as the leading contributing country and institution, respectively. Brain Stimulation ranked first in publication volume, whereas Clinical Neurophysiology received the highest citation count. The work by Rossi S. achieved the highest co-citation frequency. Current research hotspots include intermittent theta-burst stimulation, cognitive impairment, systematic review, and mild cognitive impairment.
Conclusion: Research related to TMS has been increasing annually and is a developing field. The United States leaded the way, while Harvard University was the most active institution. Daskalakis Z.J. (Canada) was the most prolific author. The most influential journals included Brain Stimulation, Clinical Neurophysiology, and Journal of Affective Disorders. Further deep collaboration among leading countries, institutions, and authors is needed. Current hotspots in TMS research involve integration with imaging techniques, clinical applications, optimization of parameters, and exploration of neurological modulation mechanisms.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; bibliometrics; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation; visualization analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Xing, Li, Huang, Xv, Yang, Li, Zhu, Shi, Meng, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Lefaucheur JP, Ayache SS, Sorel M, Farhat WH, Zouari HG, Ciampi de Andrade D, et al. Analgesic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex in neuropathic pain: influence of theta burst stimulation priming. Eur J Pain. (2012) 16:1403–13. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00150.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

