Bridging epigenetics and pharmacology through systematic reviews tailored to WBS methodology: the triangle decision-making model as a pioneering translational biological drug delivery system
- PMID: 40463968
- PMCID: PMC12130545
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1552904
Bridging epigenetics and pharmacology through systematic reviews tailored to WBS methodology: the triangle decision-making model as a pioneering translational biological drug delivery system
Abstract
Background: The health industry plays a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals, continuously driving innovations in health service delivery. Translational research fosters intimate collaboration between scientists and medical professionals. A major obstacle to effective evidence-based treatments is drug adherence, prompting the search for innovative procedures to enhance drug delivery methods.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the impact of innovative drug delivery systems (DDS) based on physical stimuli on medication adherence among patients undergoing long-term treatments. The ultimate goal was to establish a framework-based approach to assist in clinical decision-making, enhancing drug absorption efficiency.
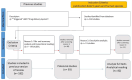
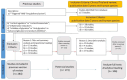
Methods: Two systematic literature reviews (SLRs) was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, focusing on DDS activated by physical and biological stimuli. The research process was structured through the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) methodology, dividing it into five interconnected Work Packages (WPs). Each WP explored specific aspects of the relationship between DDS and the human body.
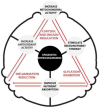
Results: The synthesis led to the development of the Triangle Decision-Making Model, a theoretical framework that prioritizes physiological balance to optimize drug delivery. The study underscores the importance of reducing insulin and cortisol levels to minimize inflammation and glycation, promoting an ideal state for drug absorption. The findings highlight the significance of using physical stimuli, such as hyperthermia, ultrasound-triggered drug delivery, and photodynamic therapy, to enhance drug bioavailability and target specificity.
Conclusions: This research proposes a novel therapeutic intervention, grounded in systematic reviews and focused on improving drug delivery via physical stimuli. Using an open innovation approach, the triangular clinical decision model integrates personalized medicine and nutraceuticals, addressing epigenetics and nutrition's role in medication response. This framework aims to enhance drug absorption, metabolism, and targeted therapies, advancing treatment outcomes. Future studies should refine this model to promote homeostasis and validate its effectiveness across healthcare settings.
Keywords: biological drug delivery system; epigenetics; inflammation reduction; medication adherence; nutraceuticals; personalized medicine; physical stimuli; translational research.
Copyright © 2025 Gaspary, Lopes and Camara.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Church D. Genie in Your Genes: Epigenetic Medicine and the New Biology of Intention. Carlsbad: Hay House Inc. (2018).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

