AMBRA1 Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression Through miR-1178/p53/CDK2-Regulated Cell Cycle Arrest
- PMID: 40464146
- PMCID: PMC12134772
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70610
AMBRA1 Inhibits Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression Through miR-1178/p53/CDK2-Regulated Cell Cycle Arrest
Abstract
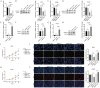
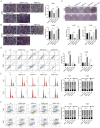
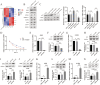
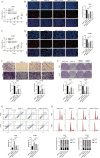
AMBRA1 is associated with a variety of pathological processes in cancer cells, but may have different functions in different tumour microenvironments or genetic backgrounds. In this study, the function and regulatory mechanisms of AMBRA1 were explored in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The abnormally expressed miRNAs in AMBRA1-overexpressed and differentially expressed genes in miR-1178-knockdown NSCLC cells were validated by RNA sequencing. Cell viability, proliferation, invasion, apoptosis, and cell cycle were tested through Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), EdU, colony formation, transwell, and flow cytometry. A mouse tumour xenograft model was conducted to assess the roles of the AMBRA1-miR-1178 axis on NSCLC progression in vivo. AMBRA1 overexpression suppressed NSCLC cell proliferation and invasion, while promoting apoptosis and G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest in vitro, and inhibited tumour growth in vivo. RNA sequencing revealed miR-1178 as a target of AMBRA1. miR-1178 overexpression partially weakened the suppressive function of AMBRA1 on cell malignant biological behaviours. p53 and CDK2 were confirmed as the downstream targets of miR-1178. Silencing p53 or overexpressing CDK2 reversed the repressive effects of AMBRA1 on the development of NSCLC cells. AMBRA1 may suppress the malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells via regulating the miR-1178-p53-CDK2 signalling pathway.
Keywords: AMBRA1; CDK2; NSCLC; cell cycle; microRNA‐1178; p53.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
circRACGAP1 Promotes Proliferation of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through the miR-1296/CDK2 Pathway.Folia Biol (Praha). 2024;70(2):104-112. doi: 10.14712/fb2024070020104. Folia Biol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 39231318
-
Acacetin inhibited non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell growth via upregulating miR-34a in vitro and in vivo.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 29;14(1):2348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52896-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38287075 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA ATP9A Stimulates Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression via MicroRNA-582-3p/Ribosomal Protein Large P0 Axis and Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 May;197(5):3166-3183. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05159-z. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39832103
-
MicroRNA-422a functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer through SULF2-mediated TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2019 Aug;18(15):1727-1744. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1632135. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Cell Cycle. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2023 May;22(9):1154. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2188818. PMID: 31204561 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Circular RNA circ_0003028 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating GOT2 via miR-1298-5p in non-small cell lung cancer.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2326-2340. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1935064. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34077306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Fuchs H. E., and Jemal A., “Cancer Statistics, 2022,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 72, no. 1 (2022): 7–33. - PubMed
-
- Sekihara K., Hishida T., Yoshida J., et al., “Long‐Term Survival Outcome After Postoperative Recurrence of Non‐Small‐Cell Lung Cancer: Who Is ‘cured’ From Postoperative Recurrence?,” European Journal of Cardio‐Thoracic Surgery 52, no. 3 (2017): 522–528. - PubMed
-
- Duma N., Santana‐Davila R., and Molina J. R., “Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment,” Mayo Clinic Proceedings 94, no. 8 (2019): 1623–1640. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

