Gene-Environment Interactions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Human Epidemiologic Studies
- PMID: 40464295
- PMCID: PMC12134891
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf061
Gene-Environment Interactions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Human Epidemiologic Studies
Abstract
Background and aims: Complex gene-environment interaction (GXE) for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remains elusive. This systematic review aims to summarize the current evidence of GXE in IBD.
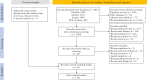
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, and Scopus were systematically searched from inception through April 30, 2024, to identify publications examining the interaction effect of genetic variants and environmental factors in IBD. All eligible studies were graded using STREGA guideline.
Results: Four thousand eight hundred thirty-three publications were identified and screened, resulting in 39 eligible studies, and 17 studies reported statistically significant interactions. NOD2-smoking interaction was most frequently investigated and showed variant-specific effect at rs2066847 regarding the risk of Crohn's disease. Gene-smoking interactions were further identified in other IBD risk genes (ATG16L1, IL23R, and CALM3), detoxification genes (GSTP1 and HMOX1), smoking-associated genes (CHRNA3, CHRNA5, PPP1R3C, and BDNF), and the inflammatory cytokine (IL1B) through a candidate gene approach. Immunochip-wide interaction analyses yielded 64 smoking interacting variants. Gene-diet interactions were observed across multiple nutritional measures, including fatty acid intake with CYP4F3 and FADS2, serum selenium with SEPHS1 and SEPSECS, potassium intake with IL21, alcohol consumption with IL12B, heme iron intake with FCGR2A, and serum vitamin D with VDR.
Conclusions: Current evidence indicated that the IBD risk conferred by environmental factors can vary among the individuals carrying certain genetic variants. Further efforts, including genome wide environment interaction studies and genotype-based nutrition/lifestyle clinical trials, are needed to unravel the missing heritability influenced by environmental exposures and to construct personalized recommendations of lifestyle/dietary modification based on an individual genetic background.
Keywords: gene-environment interaction; genetics; inflammatory bowel disease.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Conflict of interest statement
J.B. is supported by the China Scholarship Council (No. 202106210082) and University Medical Center Groningen top-up Program. E.A.M.F. received a Clinical Fellowship from the ZonMw. These sponsors have no role in the data analyses and interpretation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interventions for the management of abdominal pain in Crohn's disease and inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 29;11(11):CD013531. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013531.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34844288 Free PMC article.
-
Patient education interventions for the management of inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 4;5(5):CD013854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013854.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37172140 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for detecting colon cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9(9):CD000279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000279.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28922695 Free PMC article.
-
Incentives for preventing smoking in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD008645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008645.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28585288 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

