Organizational models and patient-reported outcomes for palliative care across five tertiary hospitals in Nigeria: An environmental scan
- PMID: 40465678
- PMCID: PMC12136337
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0004638
Organizational models and patient-reported outcomes for palliative care across five tertiary hospitals in Nigeria: An environmental scan
Abstract
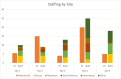
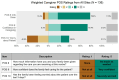
Palliative care (PC) is an essential, effective, and affordable component of health care. Global need is rising, with the greatest burden in low-and-middle-income countries. This is especially true in Nigeria where the need is growing rapidly, as are PC services; however, current organizational models have not yet been examined. This was a cross-sectional, descriptive study of five PC sites at tertiary hospitals in four of Nigeria's six geopolitical zones. Surveys, informed by a Centre for Palliative Care, Nigeria (CPCN) needs assessment checklist and the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), were administered at each site to leadership, frontline workers, patients, and caregivers. Surveys varied by participant group and inquired about organizational models and personal experiences of both providers and recipients of care. Across five sites, there was a total of 282 survey respondents: five leaders, nine frontline workers, 132 patients, and 136 caregivers. The most common diagnoses of PC patients were cancer, sickle cell disease, and HIV. Most sites reported sub-optimal administrative support (80%), hospital management support (60%), and building space (60%). Leadership responses highlighted variations in PC training requirements and opportunities. Frontline workers desired additional training, sponsorship, and governmental support. Most patients and their caregivers reported satisfaction with PC, though high levels of worry and hopelessness were reported. Increased organizational support appears necessary to facilitate improvements in administrative resources, staffing, and training. Emotional and spiritual wellbeing likely require prioritization when designing palliative care delivery services in Nigeria. Further research is needed to refine current services and inform implementation efforts.
Copyright: © 2025 Ogbenna et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Palliative care experiences of adult cancer patients from ethnocultural groups: a qualitative systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):99-111. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1809. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447011
-
Stakeholder perspectives and requirements to guide the development of digital technology for palliative cancer services: a multi-country, cross-sectional, qualitative study in Nigeria, Uganda and Zimbabwe.BMC Palliat Care. 2021 Jan 4;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12904-020-00694-y. BMC Palliat Care. 2021. PMID: 33397321 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis.In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, editors. Major Infectious Diseases. 3rd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2017 Nov 3. Chapter 11. PMID: 30212088 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Palliative care for people living with HIV/AIDS: Factors influencing healthcare workers' knowledge, attitude and practice in public health facilities, Abuja, Nigeria.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 31;14(12):e0207499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207499. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31891577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knaul FM, Bhadelia A, Rodriguez NM, Arreola-Ornelas H, Zimmermann C. The Lancet commission on palliative care and pain relief—findings, recommendations, and future directions. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;66(Suppl 1):S5–6. doi: 10.1016/s2214-109x(18)30082-2 - DOI
-
- Connor SR, Morris S, Jaramillo E. Global atlas of palliative care at the end of life. 2nd ed. World Hospice and Palliative Care Association; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
