Radioprotective effects of asiaticoside and asiatic acid in neural stem cells derived from human stem cells from apical papilla through increasing dose-reduction factor and their lowering effects on SH-SY5Y cell viability
- PMID: 40465752
- PMCID: PMC12136317
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325480
Radioprotective effects of asiaticoside and asiatic acid in neural stem cells derived from human stem cells from apical papilla through increasing dose-reduction factor and their lowering effects on SH-SY5Y cell viability
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of asiaticoside (AS) and asiatic acid (AA) against radiotherapy on neural stem cells induced from human stem cells from apical papilla (NSCs-hSCAPs) through dose-reduction factor (DRF) evaluation and their radiosensitization on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.
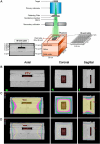
Methods: NSCs-hSCAPs were treated with AS or AA (0-500 μM) and radiation (0-8 Gy). Isolated hSCAPs were verified mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) properties according to standard protocol. Subsequently, NSCs-hSCAPs were characterized by Cresyl violet staining and immunocytochemistry. A culture plate containing the cells was embedded into the solid water and bolus phantom. After CT simulation and treatment planning, dose uniformity to the plate was evaluated. X-ray, AS, and AA toxicity were investigated using cell viability (MTT) assay. Finally, DRF50 was calculated from dose-response curves at 50% cell viability for both cell lines.
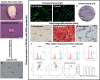
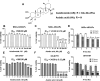
Results: hSCAPs presented MSCs markers. NSCs-hSCAPs were successfully generated due to the Nissl substance, Nestin, and SOX2 positively stained. Dose homogeneity was represented as isodose at 100% covered the cells in the phantom, suggesting that they were received according to prescribed doses. MTT results revealed that AA was more toxic than AS in both cells. X-ray reduced significantly in a number of tested cells and more radiosensitivity was observed in SH-SY5Y. However, the reduction affected by 4 Gy was diminished after AA or AS at 2 μM applied to NSCs-hSCAPs. Moreover, a significant increase of DRF50 was found at 2 μM of AA (6.72 ± 2.35) and AS (3.84 ± 1.41) in NSCs-hSCAPs whereas it did not show in SH-SY5Y. Interestingly, 20 μM AA could reduce SH-SY5Y cell viability (mean of the cell viability (%) was 25.22 ± 1.53 compared to 30.22 ± 1.46 in the control group), showing a very large in terms of its effect size (Cohen's d value = 1.37).
Conclusion: AA and AS had a specific radioprotective effect on NSCs-hSCAPs without affecting SH-SY5Y. However, AA might be a better therapeutic agent due to expressing a lethal effect on the irradiated cancer cells.
Copyright: © 2025 Tangrodchanapong et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Zhihua Y, Shoumin B, Beibei G, Shuling P, Wang L, Jun L. Radiation-induced brain injury after radiotherapy for brain tumor. In: Terry L, editor. Molecular considerations and evolving surgical management issues in the treatment of patients with a brain tumor. Rijeka: IntechOpen. 2015. p. Ch. 8.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

