Comparison of TiF4, CPP-ACP, and NaF in preventing demineralization in irradiated bovine enamel and dentin in vitro
- PMID: 40465950
- PMCID: PMC12218195
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-7757-2024-0524
Comparison of TiF4, CPP-ACP, and NaF in preventing demineralization in irradiated bovine enamel and dentin in vitro
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the effects of sodium fluoride (NaF), casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP), and titanium tetrafluoride (TiF4) on the prevention of demineralization in irradiated bovine enamel and dentin in vitro.
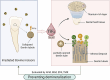
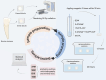
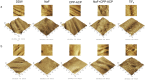
Methodology: The enamel and dentin sample blocks were subjected to 50 Gy of radiation and divided into five groups (n=13): the deionized distilled water group, the NaF group, the CPP-ACP group, the NaF + CPP-ACP group, and the TiF4 group. After being treated with various materials for 30 minutes, the samples were remineralized for 12 hours and demineralized for 48 hours. The samples were then evaluated by scanning electron microscope (SEM), atomic force microscope (AFM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and transverse microradiography (TMR). Data were analyzed by ANOVA and the Kruskal-Wallis H test (α=0.05).
Results: SEM and TMR indicated that the TiF4 group promoted more mineral deposits on the enamel and dentin samples, showing the least mineral loss and the lowest lesion depth. AFM results showed that the NaF + CPP-ACP group had the lowest enamel roughness (p<0.05), whereas the TiF4 group showed the lowest roughness in dentin samples (p<0.05). EDS showed that titanium (Ti) was deposited on the surface of the TiF4 group samples, whereas the NaF + CPP-ACP group more greatly aggregated fluorine.
Conclusion: TiF4 significantly impacted the prevention of demineralization in irradiated dental hard tissues. Combining NaF and CPP-ACP more effectively prevented demineralization than either agent used alone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

