Clinicopathological features and genomics of ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer relapsing on adjuvant abemaciclib
- PMID: 40466434
- PMCID: PMC12167084
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105126
Clinicopathological features and genomics of ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer relapsing on adjuvant abemaciclib
Abstract
Background: Two years of adjuvant abemaciclib with endocrine therapy (ET) is standard for high-risk estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, node-positive early-stage breast cancer. Relapse on adjuvant abemaciclib is poorly characterized.
Patients and methods: Patients with recurrence on adjuvant abemaciclib at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute were identified. ER, progesterone receptor (PgR), and HER2 expression pre- and post-abemaciclib was determined, and the duration of adjuvant abemaciclib, ET, and first-line metastatic treatment recorded. Genomic alterations associated with ET and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor resistance were analyzed if next-generation sequencing (NGS) was carried out at recurrence.
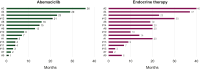
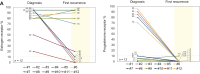
Results: Among 163 patients who received adjuvant abemaciclib (2018-2024), 15 (9.2%) experienced recurrence. Median durations were 8.0 months [interquartile range (IQR) 3.8-21.2 months] for adjuvant abemaciclib, 18.5 months (IQR 7.0-23.0 months) for adjuvant ET, and 3.0 months (IQR 1.6-5.0 months) for first-line metastatic treatment. Among 12 patients with ER, PgR, and HER2 evaluable pre- and post-abemaciclib, 6 (50.0%) with strongly positive ER at diagnosis showed ER ≤10% and PgR <1% at recurrence. Of 10 patients with NGS at recurrence, 90% had P53 pathway alterations, with one ESR1 mutation and no RB1 mutations.
Conclusions: In this series of patients relapsing on adjuvant abemaciclib plus ET, 50% showed ER loss, 90% had P53 pathway alterations, and median first-line metastatic treatment lasted 3 months.
Keywords: adjuvant abemaciclib; breast cancer; endocrine therapy; precision medicine; recurrence; translational.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Cardoso F., Spence D., Mertz S., et al. Global analysis of advanced/metastatic breast cancer: decade report (2005-2015) Breast. 2018;39:131–138. - PubMed
-
- Johnston S.R.D., Toi M., O’Shaughnessy J., et al. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(1):77–90. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rastogi P., O’Shaughnessy J., Martin M., et al. Adjuvant abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, high-risk early breast cancer: results from a preplanned monarchE overall survival interim analysis, including 5-year efficacy outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(9):987–993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turner N., Reis-Filho J., Goetz M., et al. Abstract GS03-06: Genomic and transcriptomic profiling of primary tumors from patients with HR+, HER2−, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer in the monarchE trial. Cancer Res. 2024;84(suppl 9):GS03–GS06.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

