Reduction of SEM charging artefacts in native cryogenic biological samples
- PMID: 40467589
- PMCID: PMC12137866
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60545-3
Reduction of SEM charging artefacts in native cryogenic biological samples
Abstract
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of frozen-hydrated biological samples allows imaging of subcellular structures at the mesoscale in a representation of their native state. Combined with focused ion beam milling (FIB), serial FIB/SEM can be used to build a 3-dimensional model of cells and tissues. The correlation of specific regions of interest with cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) can additionally enable subsequent high-resolution analysis. However, the use of serial FIB/SEM imaging-based methods is often limited due to charging artefacts arising from insulating areas of cryogenically preserved samples. Here, we demonstrate the use of interleaved scanning to attenuate these artefacts, allowing the observation of biological features that otherwise would be masked or distorted. We apply our method to samples where inherent features were not visible using conventional scanning. These examples include membrane contact sites within mammalian cells, visualisation of the degradation compartment in the algae E. gracilis and observation of a network of membranes within different types of axons in an adult mouse cortex. The proposed alternative scanning method could also be applied to imaging other non-conductive specimens in SEM.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
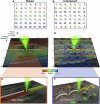

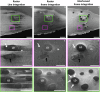


Similar articles
-
Cryo-plasma FIB/SEM volume imaging of biological specimens.Elife. 2023 Feb 21;12:e83623. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83623. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36805107 Free PMC article.
-
A protocol for cryogenic volumetric imaging using serial plasma FIB/SEM.Methods Cell Biol. 2023;177:327-358. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2023.01.015. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Methods Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37451772
-
An introduction to cryo-FIB-SEM cross-sectioning of frozen, hydrated Life Science samples.J Microsc. 2021 Feb;281(2):138-156. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12951. Epub 2020 Aug 24. J Microsc. 2021. PMID: 32737879 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-focused-ion-beam applications in structural biology.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Sep 1;581:122-30. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25703192 Review.
-
Advances, challenges, and applications of cryo-electron tomography workflows for three-dimensional cellular imaging of infectious pathogens.J Microsc. 2025 Apr 1. doi: 10.1111/jmi.13408. Online ahead of print. J Microsc. 2025. PMID: 40165665 Review.
References
-
- Angert, I., Burmester, C., Dinges, C., Rose, H. & Schröder, R. R. Elastic and inelastic scattering cross-sections of amorphous layers of carbon and vitrified ice. Ultramicroscopy63, 181–192 (1996).
-
- Wong, W. K., Thong, J. T. L. & Phang, J. C. H. Charging identification and compensation in the scanning electron microscope. In Proc 1997 6th International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits 97–102 (IEEE). 10.1109/IPFA.1997.638151.
-
- Krakow, W. & Nixon, W. C. The behavior of charged particles in the scanning electron microscope. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl.IA-13, 355–366 (1977).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

