Early hemodynamic differences between generalized and focal epilepsy measured by photoplethysmography
- PMID: 40467660
- PMCID: PMC12137735
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02127-3
Early hemodynamic differences between generalized and focal epilepsy measured by photoplethysmography
Abstract
Photoplethysmography (PPG) detects hemodynamic changes during epileptic seizures. This study aim to investigate PPG signals changes during generalized tonic‒clonic seizures (GTCSs) and focal impaired awareness seizures (FIASs). 17 GTCS and 19 FIAS episodes were recorded from 18 patients. The 30 min preictal period was divided into three 10-minute intervals. PPG features analyzed were pulse upslope (PUS), maximal compliance (Kmax), and skewness. Features across 3 preictal intervals showed significant reductions compared to the baseline: PUS (F(3,64) = 11.870, p < 0.001), Kmax (F(3,64) = 7.419, p < 0.001) and skewness (F(3,64) = 2.852, p = 0.044) in the GTCS group. PUS (Kruskal-Wallis [K-W] = 22.600, p < 0.001) and Kmax (K-W = 28.110, p < 0.001) in the FIAS group. In the GTCS group, the largest difference was observed 30 min before seizure onset (PUS: p < 0.001, Cohen's d = 1.843; Kmas: p < 0.001, Cohen's d = 1.419; skewness: p = 0.043, Cohen's d = 0.808), whereas this was not the case in the FIAS group. PPG signals showed earlier changes in the GTCS group than in the FIAS group, highlighting their differences and the potential of PPG-based monitoring for early seizure detection.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Focal impaired awareness seizures; Generalized tonic‒clonic seizures; Photoplethysmography.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
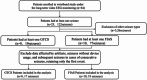
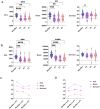

References
-
- Fisher, R. S. et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE commission for classification and terminology. Epilepsia58 (4), 522–530 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Elger, C. E. & Hoppe, C. Diagnostic challenges in epilepsy: seizure under-reporting and seizure detection. Lancet Neurol.17 (3), 279–288 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Beniczky, S. et al. Automated seizure detection using wearable devices: A clinical practice guideline of the international league against epilepsy and the international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Epilepsia62 (3), 632–646 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

