SFXN1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by restraining PINK1-dependent mitophagy
- PMID: 40468051
- PMCID: PMC12318774
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-025-03460-7
SFXN1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by restraining PINK1-dependent mitophagy
Abstract
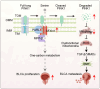
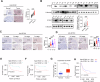
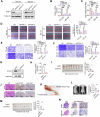
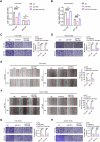
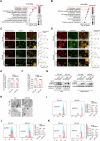
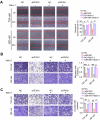
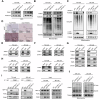
Sideroflexin 1 (SFXN1), a newly identified mitochondrial serine transporter, exhibits great potential to modulate mitochondrial function and promote tumor development. However, its role in bladder cancer (BLCA) remains unclear. Our study revealed that SFXN1 was enriched in clinical BLCA tissues, and high SFXN1 expression in BLCA was positively associated with the progression and poor prognosis. Further, SFXN1 deficiency remarkably suppressed the proliferation and metastasis of BLCA cells in vitro and in vivo, indicating an oncogenic role of SFXN1 in BLCA. Additionally, our results demonstrated that SFXN1 promotes metastasis through its unknown function of restraining PINK1 (PTEN-induced kinase 1)-dependent mitophagy rather than its classical role as a mitochondrial serine transporter to mediate one-carbon metabolism. Mechanistically, SFXN1 acted as a bridge to promote PINK1 degradation by interacting with PARL (presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein) and MPP-β (mitochondrial processing peptidase-β), leading to mitophagy arrest. Notably, when mitophagy was restrained by highly-expressed SFXN1, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species were considerably enriched, thus activating TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β)-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promoting metastasis of BLCA cells. This study highlights SFXN1 as a novel promising therapeutic target for BLCA and identifies a new mitophagic modulator to improve our understanding of an association between mitophagy and BLCA progression. Schematic diagram of the proposed mechanism by which SFXN1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by restraining PINK1-dependent mitophagy. SFXN1 is upregulated in BLCA tissues, and promotes BLCA metastasis through its unrevealed function of restraining PINK1-dependent mitophagy rather than its classical role as a mitochondrial serine transporter to promote cell proliferation. Specifically, SFXN1 acted as an essential bridging factor to promote PINK1 degradation by interacting with PARL and MPP-β on the IMM, leading to mitophagy arrest and mtROS accumulation, thus activated TGF-β-mediated EMT and promoted BLCA metastasis (This figure was created by Figdraw).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All study participants provided informed consent, and the study design was approved by Institutional Ethics Committee of the Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital approved this study (2022-493-01). All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DSG3 promotes bladder cancer growth and metastasis via AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 2;23(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06754-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40605005 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin Inhibits Bladder Cancer Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis and Cycle Arrest by PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a and ER Stressmitochondria Pathways.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(19):3879-3904. doi: 10.2174/0109298673283888231217174702. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38357946
-
Spautin-1 promotes PINK1-PRKN-dependent mitophagy and improves associative learning capability in an alzheimer disease animal model.Autophagy. 2024 Dec;20(12):2655-2676. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2383145. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 39051473 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 2017;71:96–108. - PubMed
-
- Jubber I, Ong S, Bukavina L, Black PC, Compérat E, Kamat AM, et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer in 2023: a systematic review of risk factors. Eur Urol. 2023;84:176–90. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, Rowland JH, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:271–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

