HLN-DDI: hierarchical molecular representation learning with co-attention mechanism for drug-drug interaction prediction
- PMID: 40468206
- PMCID: PMC12135231
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-025-06157-6
HLN-DDI: hierarchical molecular representation learning with co-attention mechanism for drug-drug interaction prediction
Abstract
Background: Accurate identification of drug-drug interactions (DDIs) is critical in pharmacology, as DDIs can either enhance therapeutic efficacy or trigger adverse reactions when multiple medications are administered concurrently. Traditional methods for identifying DDIs are labor-intensive and time-consuming, prompting the development of computational alternatives. However, existing computational approaches frequently encounter challenges related to interpretability and struggle to effectively capture the complex, multi-level structures inherent in drug molecules. Specifically, they often fail to adequately analyze substructural components and neglect interactions across hierarchical structural levels, resulting in incomplete molecular representations.
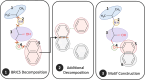
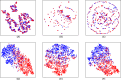
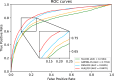
Results: In this study, we propose a Hierarchical Learning Network with a co-attention mechanism tailored to molecular structure representation for predicting DDIs, named HLN-DDI. The proposed method advances existing approaches by explicitly encoding motif-level structures and capturing hierarchical molecular representations at atom-level, motif-level, and whole-molecule scales. These hierarchical representations are integrated using a co-attention mechanism and combined with interaction-type information to enhance predictive performance. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that HLN-DDI significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple benchmark datasets, achieving over 98% accuracy under transductive scenarios and surpassing 99% on various evaluation metrics. Moreover, HLN-DDI achieves a notable accuracy improvement of 2.75% in predicting DDIs involving unseen drugs. Practical assessments with real-world DDI scenarios further validate the efficacy and utility of our proposed model.
Conclusion: By leveraging hierarchical molecular structures and employing a co-attention mechanism to effectively integrate multi-level representations, HLN-DDI generates comprehensive and precise drug representations, leading to substantially improved predictions of potential drug-drug interactions.
Keywords: Co-attention mechanism; Drug-drug interaction; Molecular graph learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dale MM, Haylett DG. Rang & Dale’s pharmacology flash cards updated edition e-book. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013.
-
- Wienkers LC, Heath TG. Predicting in vivo drug interactions from in vitro drug discovery data. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(10):825–33. - PubMed
-
- Juurlink DN, Mamdani M, Kopp A, Laupacis A, Redelmeier DA. Drug-drug interactions among elderly patients hospitalized for drug toxicity. JAMA. 2003;289(13):1652–8. - PubMed
-
- Yeh P, Tschumi AI, Kishony R. Functional classification of drugs by properties of their pairwise interactions. Nat Genet. 2006;38(4):489–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

