HS-10375, a selective EGFR C797S tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40468352
- PMCID: PMC12135467
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06613-0
HS-10375, a selective EGFR C797S tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The C797S mutation is one of the most common mechanisms of acquired resistance to third generation EGFR TKIs, yet no approved therapies have been available to target it. Here we developed a novel selective EGFR C797S inhibitor, HS-10375, and report the results of pre-clinical research and the first-in-human phase 1 trial.
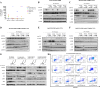
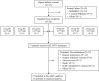
Methods: Ba/F3 cell lines and patient-derived cells expressing mutant EGFR were used to test the selectively inhibitory potency of HS-10375 in vitro, and cell line-derived xenograft animal models were used to evaluate the anticancer efficacy of HS-10375 in vivo. In the phase 1 trial, HS-10375 was administered orally at six dose levels (10-240 mg) daily (QD) in 21-day cycles, following a rule-based, rolling six design. The primary objectives were the safety, tolerability and maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The secondary objectives included PK parameters and anti-tumor activity.
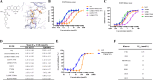
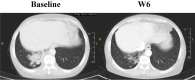
Results: HS-10375 showed more potent activity in inhibiting EGFR phosphorylation compared to 1st to 3rd generation EGFR TKIs in C797S triple-mutant cell lines. HS-10375 also exhibited comparable inhibitory activity to 1st- and 2nd- generation EGFR TKIs and superior activity to 3rd-generation EGFR TKIs in C797S double-mutant cell lines. Furthermore, cells harboring EGFR double or triple C797S mutation underwent remarkable apoptosis upon HS-10375 treatment. HS-10375 effectively inhibited tumor growth in C797S triple-mutant mouse models. In the first-in-human trial, 28 patients with advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancers who harbored EGFR mutation and who had experienced treatment failure with EGFR TKI treatment received at least one dose of HS-10375. Dose-limiting toxicities were observed in 2 patients at 240 mg QD, and MTD was reached at HS-10375 150 mg QD. The most common treatment-related adverse events were vomit (37.0%), loss of appetite (33.3%), and elevated AST (33.3%). One patient with EGFR mutations showed tumor shrinkage after progression on five-line treatment including gefitinib, almonertinib, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and EGFRxHER3 antibody-drug conjugate.
Conclusions: HS-10375 demonstrated potent and mutant-selective activity against the EGFR C797S mutation in preclinical results, and showed an acceptable safety profile and objective response in a first-in-human phase 1 trial. Trial registration This trial is registered on China Drug Trials (CTR20220045), and ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05435248).
Keywords: C797S mutation; EGFR TKI; HS-10375; Non-small cell lung cancer; Targeted therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This clinical trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (A2021-184–01). Informed consent was provided by all recruited subjects prior to the study. Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication of individual data was obtained from all patients. Competing interests: W.X., Yan Yang, Z.C., B.S., D.S., X.S. and P.G. are the employees of Hansoh Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–54. - PubMed
-
- Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS. Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med. 2020;41(1):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Yoneda K, Imanishi N, Ichiki Y, Tanaka F. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR-mutations. J uoeh. 2019;41(2):153–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 82272789/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82241232/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82473346/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202206010141/Guangzhou Science and Technology Project
- 2024ZD0519700/Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases National Science and Technology Major Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

