Unlocking the life code: a review of SnoRNA functional diversity and disease relevance
- PMID: 40468441
- PMCID: PMC12135493
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02274-0
Unlocking the life code: a review of SnoRNA functional diversity and disease relevance
Abstract
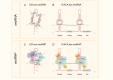
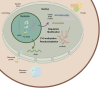
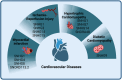
Nucleolar small RNA (snoRNA), as a class of non-coding RNAs, play a crucial role in eukaryotic cells. They are widely involved in post-transcriptional modifications of ribosomal RNAs, including methylation and pseudouridylation, precisely regulating the process of ribosome biogenesis, ensuring the integrity of ribosome structure and function, and thereby guaranteeing the accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis. snoRNAs not only maintain cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation under normal physiological conditions but also have abnormal expression closely associated with various diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. In recent years, with the innovation of research techniques, there has been a deeper exploration of the biosynthesis pathways, functional mechanisms of snoRNAs, and their potential value in disease diagnosis and treatment. This review comprehensively summarizes the structural characteristics, classification systems, biological functions, and disease associations of snoRNAs, and looks forward to future research directions, aiming to provide a systematic reference for further exploration of the mysteries of snoRNAs in related fields.
Keywords: Cancer; Cardiovascular diseases; Neurodegenerative diseases; Nucleolar small RNAs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

