Smi-miRmTERF regulates organelle development, retrograde signaling, secondary metabolism and immunity via targeting a subset of SmmTERFs in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- PMID: 40468467
- PMCID: PMC12139070
- DOI: 10.1186/s43897-025-00153-3
Smi-miRmTERF regulates organelle development, retrograde signaling, secondary metabolism and immunity via targeting a subset of SmmTERFs in Salvia miltiorrhiza
Abstract
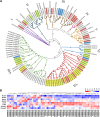
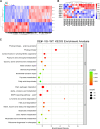
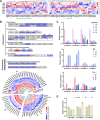
MicroRNAs are a class of endogenous small non-coding RNAs, some of which can trigger phased secondary small interfering RNA (phasiRNA) production from target genes. Mitochondrial transcription termination factors (mTERFs), mainly localized in chloroplasts and/or mitochondria, play critical roles in plant development and stress responses. We report here the identification of 63 mTERFs and a 22 nt novel miRNA (smi-miRmTERF), which directly cleave SmmTERF33 and SmmTERF45 transcripts to trigger phasiRNA biogenesis. The generated phasiRNAs could further trigger phasiRNA biogenesis from SmmTERF26 and regulated a subset of lineage-specific SmmTERFs. MIRmTERF widely existed in Nepetoideae plants and SmmTERF33 and SmmTERF45 proteins were localized in chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the cytoplasm. Smi-miRmTERF overexpression (MIRMTERF#OE) resulted in a dwarfing phenotype with severe defects in chloroplast and mitochondrial morphogenesis. Transcriptomic analysis showed up-regulation of defense-related and down-regulation of photosynthesis-related genes in MIRMTERF#OE plants. Under norflurazon and lincomycin treatments, MIRMTERF#OE plants displayed a gun phenotype, indicating the role of smi-miRmTERF in retrograde signaling. Furthermore, MIRMTERF#OE plants showed increased contents of phenolic acids, monoterpenoids, and sesquiterpenoids and reduced susceptibility to pathogenic bacteria Pst DC3000. The results suggest that smi-miRmTERF is a significant regulator of chloroplast and mitochondrial development, retrograde signaling, secondary metabolism, and immunity in S. miltiorrhiza.
Keywords: Salvia miltiorrhiza; SmmTERFs; immune response; miRmTERF; phasiRNA; retrograde signaling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC. MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell. 2005;121:207–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
