In vivo evaluation of population-specific inversion pulses in parallel transmission
- PMID: 40468560
- PMCID: PMC12393190
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.30593
In vivo evaluation of population-specific inversion pulses in parallel transmission
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the study was to conduct in vivo evaluation of population-specific pulses in the context of the MP2RAGE sequence for brain imaging at 7T.
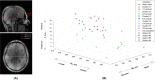
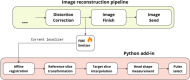
Methods: Five clusters were identified in a cohort of 39 volunteers. One cluster centered around the average head shape and position, whereas four others were located toward the extremes of the population distribution. Additionally, the one-size-fits-all solution was considered, using a standard universal pulse (UP) approach. Head shapes were characterized using lateral head breadth (HB), anterior-posterior head length (HL), and Y-shift metrics. For each group, a 5kT-points universal inversion pulse was computed and evaluated on four new test anatomies. A Python pipeline was integrated into the image reconstruction routine, using localizer scans to classify head shapes and positions. The pipeline selected one of five precomputed population-specific pulses or defaulted to the generic UP without extending scan time.
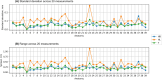
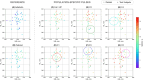
Results: The pipeline accurately classified head shapes and selected suitable pulses, enhancing the contrast of MP2RAGE images. Population-specific pulses helped mitigate some of the performance loss associated with using a one-size-fits-all UP, bringing performance closer to that of fully tailored solutions. This approach was particularly beneficial for individuals with smaller head sizes. However, the performance was worse in larger, more challenging head shapes.
Conclusion: The novel head clustering and pulse selection pipeline facilitates the implementation of population-specific pulses in clinical practice by allowing pulse selection tailored to each head shape and position without increasing scan time.
Keywords:
© 2025 The Author(s). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Simon Lévy, Kelvin Chow and Patrick Liebig are employees of Siemens Healthcare.
Figures

References
-
- Ladd ME, Bachert P, Meyerspeer M, et al. Pros and cons of ultra‐high‐field MRI/MRS for human application. Prog Nuclear Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2018;109:1‐50. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan JT, Garwood M, Collins CM, et al. 7T vs. 4T: RF power, homogeneity, and signal‐to‐noise comparison in head images. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:24‐30. - PubMed
-
- Brink JS. Thermal effects associated with RF exposures in diagnostic MRI: overview of existing and emerging concepts of protection. Concepts Magn Reson Part B. 2019;2019:1‐17.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

