Hyaluronic acid-engineered milk extracellular vesicles to target triple negative breast cancer through CD44
- PMID: 40468893
- PMCID: PMC12143002
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2511807
Hyaluronic acid-engineered milk extracellular vesicles to target triple negative breast cancer through CD44
Abstract
Context: Cancer therapy remains a challenge in healthcare, particularly in the context of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), where targeted therapies are still scarce.
Objective: Addressing this issue, our study explores a novel targeting approach using small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) isolated from cow milk, functionalized with hyaluronic acid (HA) to target the overexpressed cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) cell surface receptor in TNBC cells.
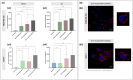
Materials & methods: A method for isolating sEVs from cow milk was optimized, and the obtained sEVs were fully characterized in terms of size, morphology, and protein markers. Subsequently, milk-derived sEVs were covalently bound with HA of varying molecular weights (MW, 20-60 kDa, 250 kDa, 1000-1600 kDa) and binding and internalization dynamics were investigated. Breast cancer cell lines, MDA-MB-231 (TNBC and CD44+) and MCF-7 (CD44-), were used as in vitro models to evaluate CD44 selectivity.
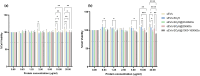
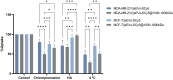
Results: The binding and internalization studies unveiled enhanced selectivity of functionalized sEVs for CD44-overexpressing cells compared to non-functionalized sEVs. Notably, higher MW HA exhibited enhanced binding capacity, with partial internalization occurring through CD44 endocytic mechanisms.
Discussion and conclusion: In summary, this work introduces a sEVs isolation method and sheds light on the role of HA MW in enhancing cellular uptake of CD44 overexpressing cancer cells.
Keywords: Bovine milk; CD44; breast cancer; hyaluronic acid; selective targeting; small extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Arntz OJ, Pieters BCH, Oliveira MC, Broeren MGA, Bennink MB, de Vries M, van Lent PLEM, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB, van der Kraan PM, et al. 2015. Oral administration of bovine milk derived extracellular vesicles attenuates arthritis in two mouse models. Mol Nutr Food Res. 59(9):1701–1712. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500222. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
