Efficacy and Safety of Combining r-ATG With PTCy for GvHD Prophylaxis in Haploidentical HSC Transplantation for Malignancies-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40469057
- PMCID: PMC12138436
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70450
Efficacy and Safety of Combining r-ATG With PTCy for GvHD Prophylaxis in Haploidentical HSC Transplantation for Malignancies-A Systematic Review
Abstract
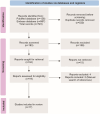
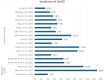
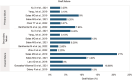
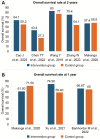
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for haematological malignancies can cause acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), impacting graft success and mortality. Rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (r-ATG) or post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) is effective in reducing GvHD in haploidentical-HSCT. This review included 17 studies to assess rATG + PTCy for GvHD prophylaxis. Overall acute GvHD grade II-IV, moderate-to-severe chronic GvHD and GvHD-free relapse-free survival rates ranged from 11.50%-35.40%, 2.90%-17.78% and 21.80%-63%, respectively. Although r-ATG + PTCy treatment lowered GvHD incidence and increased survival rates, cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation were observed; therefore, more investigations on this treatment are needed, especially on dosing and timing when used for HSCT.
Keywords: anti‐thymocyte globulin (rATG); cyclophosphamide; graft vs. host disease (GvHD); haematopoietic stem cell transplantation; haploidentical.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wu K. H., Weng T. F., Li J. P., and Chao Y. H., “Antithymocyte Globulin Plus Post‐Transplant Cyclophosphamide Combination as an Effective Strategy for Graft‐Versus‐Host Disease Prevention in Haploidentical Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation for Children With High‐Risk Malignancies,” Pharmaceuticals 15 (2022): 1423. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Law A. D., Salas M. Q., Lam W., et al., “Reduced‐Intensity Conditioning and Dual T Lymphocyte Suppression With Antithymocyte Globulin and Post‐Transplant Cyclophosphamide as Graft‐Versus‐Host Disease Prophylaxis in Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants for Hematological Malignancies,” Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 24 (2018): 2259–2264. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stocker N., Gaugler B., Labopin M., et al., “High‐Dose Post‐Transplant Cyclophosphamide Impairs γδ T‐Cell Reconstitution After Haploidentical Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Using Low‐Dose Antithymocyte Globulin and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Graft,” Clinical & Translational Immunology 9 (2020): e1171. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barkhordar M., Kasaeian A., Janbabai G., et al., “Modified Combination of Anti‐Thymocyte Globulin (ATG) and Post‐Transplant Cyclophosphamide (PTCy) as Compared With Standard ATG Protocol in Haploidentical Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Leukemia,” Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 921293. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

