Single arm meta-analysis of the J-Valve system for aortic regurgitation in Chinese populations
- PMID: 40469077
- PMCID: PMC12133853
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1436789
Single arm meta-analysis of the J-Valve system for aortic regurgitation in Chinese populations
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of J-valve in patients with Aortic regurgitation (AR).
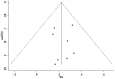
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched from inception to November 2024. Primary outcome included Procedural Success, and secondary outcome included In-Hospital Mortality, 30-Day Mortality, One-Year All-Cause Mortality, Stroke Incidence and Complications. The risk of bias was assessed by subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, and publication bias, including funnel plot, Egger's test, and Begg's test.
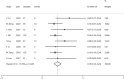
Results: A total of 9 studies involving 552 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The results indicated a surgical success rate of 96% (95% CI: 0.94-0.99). The in-hospital mortality rate was 3% (95% CI: 0.01-0.04), the 30-day mortality rate was 3% (95% CI: 0.01-0.05), and the 1-year all-cause mortality rate was 6% (95% CI: 0.04-0.08). Additionally, the incidence of stroke was 2% (95% CI: 0.01-0.03), and the incidence of other complications was 22% (95% CI: 0.16-0.28).
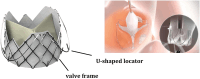
Conclusions: This meta-analysis indicates that the J-Valve prosthesis exhibits favorable short-term efficacy in patients with severe aortic regurgitation (AR); however, a significant incidence of complications persists. A thorough risk assessment is crucial when determining the appropriate treatment strategy. Furthermore, postoperative follow-up duration should be extended to monitor patient outcomes effectively.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024552406, identifier CRD42024552406.
Keywords: Chinese; J-Valve; aortic regurgitation (AR); cardiac valve; meta-analysis.
© 2025 Gao, Mao, Zeng and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors wish to express sincere gratitude to Prof. Xuan Xiong for her valuable contributions to manuscript revision and technical discussions.The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

