Cross-reactivity and sensitization profiles of cockroach and moth allergens provide new insights in cockroach-allergic patients
- PMID: 40469215
- PMCID: PMC12133693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2025.101057
Cross-reactivity and sensitization profiles of cockroach and moth allergens provide new insights in cockroach-allergic patients
Abstract
Background: Inhalant insect allergens are widely implicated as common triggers of respiratory allergies, but little is known about cross-reactivity between cockroaches and other insect allergens. This study mainly investigates sensitization profiles and cross-reactivity between cockroach allergens and moth allergens to provide insights into the clinical management of cockroach-allergic patients.
Methods: A total of 386 suspected cockroach-sensitized patients were enrolled. Sensitization rates were determined using IgE testing for common airborne allergens. Cross-reactivity was evaluated using IgE inhibition assays, immunoblotting, and basophil activation tests. Age-related sensitization patterns were analyzed to assess variability in immune response across different demographics.
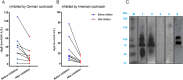
Results: A high frequency of silk moth was observed in cockroach-sensitized patients, with sensitization rates to German cockroach and silk moth allergens at 81.09% and 81.61%, respectively, and a high co-sensitization rate (54.66%). Age analysis revealed similar peak sensitization of German cockroach and silk moth in school-age children and young adults, with a lower prevalence in the elderly. Additionally, cockroach crude extract can inhibit the IgE-binding of cockroach-sensitized patients' sera and silk moth crude extract, while various moths can activate basophils as well.
Conclusions: This study highlights the similar age-related sensitization patterns between German cockroach and silk moth, differing from those observed with house dust mites. Besides, cross-reactivity between different cockroach and moth allergens was confirmed through significant IgE inhibition, multiple sequences alignment of shared epitopes and basophil activation tests. These findings highlight the need to consider cross-reactivity between cockroach and moth allergens in clinical evaluations.
Keywords: Blattella germanica (German cockroach); Cockroach allergy; Cross-reactivity; Insect allergen; Silk moth.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence of sensitivity to cockroach allergens and IgE cross-reactivity between cockroach and house dust mite allergens in Chinese patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Dec;123(24):3540-4. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 22166627
-
Shrimp and cockroach co-sensitization in Southern China: Association with moth sensitization.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2020 May 1;41(3):e54-e60. doi: 10.2500/aap.2020.41.200013. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2020. PMID: 32375970
-
Allergen content in German cockroach extracts and sensitization profiles to a new expanded set of cockroach allergens determine in vitro extract potency for IgE reactivity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr;143(4):1474-1481.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.07.036. Epub 2018 Aug 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30170124 Free PMC article.
-
[Cockroach allergy: a study of its prevalence using skin tests with commercial extracts].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 1995 Nov-Dec;23(6):295-300. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 1995. PMID: 8579009 Review. Spanish.
-
The effect of immunotherapy on cross-reactivity between house dust mite and other allergens in house dust mite -sensitized patients with allergic rhinitis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Sep;17(9):969-975. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1968834. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34388949 Review.
References
-
- Han W., Qiu L., Zhang J., et al. Phylogenetic reconstruction of Corydioidea (Dictyoptera: Blattodea) provides new insights on the placement of Latindiinae and supports the proposal of the new subfamily Ctenoneurinae. Syst Entomol. 2023;49(1):156–172. doi: 10.1111/syen.12610. - DOI
-
- Helm R.M., Squillace D.L., Jones R.T., et al. Shared allergenic activity in Asian (Blattella asahinai), German (Blattella germanica), American (Periplaneta americana), and Oriental (Blatta orientalis) cockroach species. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;92(2):154–161. doi: 10.1159/000235207. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

