Intergenerational and transgenerational effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the offspring brain development and behavior
- PMID: 40469448
- PMCID: PMC12133532
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1571689
Intergenerational and transgenerational effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the offspring brain development and behavior
Abstract
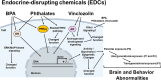
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are a group of substances that can alter normal body functioning by disrupting the various patterns of hormone secretion and action. Some of these substances are used as plasticizers (e.g., bisphenols and phthalates) and agrochemicals (e.g., vinclozolin). EDC exposure can occur by many routes, including oral by contaminated food and water, through the skin, inhalation, and by placental transfer from mother to fetus or mother to infant (via lactation). The increase in EDCs used by the industry has strongly impacted our health. An increasing number of scientific works have reported the effects of EDCs on cancer development, metabolism, heart disease, and fertility. Most recently, studies on EDCs effects on behavior and the developing brain are raising major concerns related to the formation of sex differences and to the increased prevalence of neuropsychiatric disorders. In this review, we highlight the recent findings of the effects of pre-, peri-, and postnatal exposure to the three well-studied EDCs (i.e., bisphenols (BPA, BPS, BPF, and BPAF), phthalates (DBP, BBP, DEHP, and DiPeP), and vinclozolin (VIN)) on developing brain and behavior across generations in experimental animals.
Keywords: BPA; BPAF; BPF; behavior; bps; endocrine-disrupting chemicals; phthalates; vinclozolin.
Copyright © 2025 Dias, Giusti, de Novais, de Oliveira, Paiva, Kalil-Cutti, Mahoney and Graceli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Colborn T, vom Saal FS, Soto AM. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. In: The Embryo Project Encyclopedia (1993). Rio de Janeiro, Brasil: Available at: https://embryo.asu.edu/pages/developmental-effects-endocrine-disrupting-.... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

