Associations between Life's Essential Eight cardiovascular health metrics and cardiovascular mortality risk across frailty statuses: evidence from a UK Biobank cohort study
- PMID: 40469586
- PMCID: PMC12133463
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1508274
Associations between Life's Essential Eight cardiovascular health metrics and cardiovascular mortality risk across frailty statuses: evidence from a UK Biobank cohort study
Abstract
Background: Higher cardiovascular health (CVH) scores are related to lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality, and frailty status may moderate the association. Whether the associations of Life's Essential 8 (LE8) with mortality from CVD and its subtypes differ across frailty status remains unknown. Therefore, we aimed to assess the association between LE8 and CVD mortality among individuals with different frailty status.
Methods: Data were sourced from the UK Biobank of 439,462 participants aged 37-73 years. LE8, as a metric of CVH, was assessed using four health behaviors (diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure, and sleep health) and four health factors (body mass index, blood lipids, blood glucose, and blood pressure). Frailty status was measured with frailty index (FI) and Fried phenotype (FP). The outcomes included mortality of CVD, coronary heart disease, and cerebrovascular disease. Cox regression was used to calculate hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) to assess the association, and additive and multiplicative interactive effects were also examined.
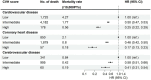
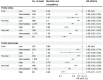
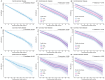
Results: Over a median follow-up period of 13.7 [interquartile range 13.0-14.4] years, 6,085 participants died from CVD. The moderate or high level of LE8 lowered the risk of CVD mortality with HRs (95% CIs) of (0.50, 0.47-0.53) and (0.25, 0.22-0.29), respectively. The effect did not differ in individuals with different frailty status (Pinteraction > 0.05), each group with an HR of about 0.3. Compared with those with low LE8 and frail, the HR for individuals who are not frail and with high LE8 level was about 0.15. Similar results were found for endpoints of CVD subtypes and for participants of all ages and sexes, and specifically, CVH appeared to be better protected for CVD mortality in those who were not treated for blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
Conclusion: Ideal CVH was associated with lower risk of CVD mortality regardless of frailty status. Specifically, for frail participants, optimizing CVH is a cost-effective strategy to mitigate CVD risk and promote healthy ageing.
Keywords: cardiovascular health; cardiovascular mortality risk; cohort study; frailty; survival analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Chai, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Zhang and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular health and cancer mortality: evidence from US NHANES and UK Biobank cohort studies.BMC Med. 2024 Sep 5;22(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03553-2. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39237921 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Life's Essential 8 with incidence of heart failure modified by depressive symptoms: a prospective cohort study from UK Biobank.BMC Med. 2025 Mar 24;23(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04011-3. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40128779 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of Life's Essential 8 to the genetic predisposition for cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality: results from a national prospective cohort.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023 Oct 26;30(15):1676-1685. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwad179. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37228091
-
Life's Essential 8 and the risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Apr 2;32(5):358-373. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae280. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39171613
-
Dose-response associations of the American Heart Association's new "Life's essential 8" metrics with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a nationally representative sample from the United States.Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Jul-Aug;85:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2024.06.001. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38925257 Review.
References
-
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403:2100–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Allen NB, Anderson CAM, Black T, Brewer LC, Foraker RE, et al. . Life's essential 8: updating and enhancing the American Heart Association's construct of cardiovascular health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 146:e18–43. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, et al. . Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. (2010) 121:586–613. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192703, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petermann-Rocha F, Deo S, Celis-Morales C, Ho FK, Bahuguna P, McAllister D, et al. . An opportunity for prevention: associations between the Life's essential 8 score and cardiovascular incidence using prospective Data from UK biobank. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2023) 48:101540. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101540, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

