Coptis japonica Makino ethanol extracts attenuates cancer cachexia induced muscle and fat wasting through inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40469669
- PMCID: PMC12133494
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1509086
Coptis japonica Makino ethanol extracts attenuates cancer cachexia induced muscle and fat wasting through inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
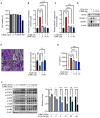
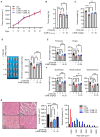
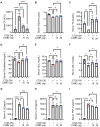
Cancer cachexia is a complex syndrome marked by appetite loss, weakness, fatigue, significant weight loss, and depletion of both adipose and muscle tissue, driven by metabolic and inflammatory alterations caused by tumors. Cachexia is a critical contributor to poor cancer prognosis, often leading to reduced efficacy of treatments. Coptis japonica Makino (CJM) is a medicinal herb widely used in Asia, known for its anti-inflammatory and metabolic regulatory properties. However, its potential role in cancer cachexia has not yet been explored. This research aimed to explore the potential of CJM extracts (CJME) in mitigating cancer cachexia in both myotubes treated with CT26 conditioned medium (CM) and in a CT26-induced cancer cachexia mouse model. Our results demonstrated that CJME significantly decreased the mRNA and protein levels of muscle-specific E3 ubiquitin ligases Atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in myotubes exposed to CT26 CM. Furthermore, CJME notably enhanced the protein levels of myosin heavy chain (MyHC). In the mouse model of CT26-induced cancer cachexia, severe loss of muscle and fat was observed. however, CJME effectively countered this wasting and restored abnormal biochemical parameters such as CK, albumin, triglycerides (TG), cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) associated with cancer cachexia. Moreover, CJME reduced interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in both CT26 CM-stimulated myotubes and the serum of CT26-induced cancer cachexia mice. The mechanism underlying these effects appears to involve the suppression of STAT3 activation by CJME. These findings suggest that CJME has potential as a therapeutic candidate in the management of cancer cachexia.
Keywords: Coptis japonica Makino; IL-6; STAT3; cancer cachexia; muscle atrophy.
Copyright © 2025 Hwang, Park, Han, Yoon, Jang, Lim, Park, Park, Cho and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

