Matrix gla protein mediates CD8+ T-cell exhaustion to facilitate immune evasion in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 40469710
- PMCID: PMC12134819
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_232_2024
Matrix gla protein mediates CD8+ T-cell exhaustion to facilitate immune evasion in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Matrix Gla protein (MGP) has been found to be strongly associated with cancer progression. However, its role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) remains unclear, particularly within the tumor immune microenvironment. MGP may promote immune evasion by activating the nuclear factor-kappa-light-chain-enha ncer of activated B-cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which increases the expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and contributes to CD8+ T-cell exhaustion. This research mainly aims to examine the regulatory role of MGP in immune evasion in ICC.
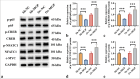
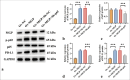
Material and methods: ICC xenograft mouse models and human ICC cell line (HuCCT1) cell models were established to evaluate MGP expression patterns. MGP knockdown or overexpression in HuCCT1 cells was co-incubated with antigen-specific CD8+ T cells, and flow cytometry was used to detect markers of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion. The effects of MGP modulation on PD-L1 expression were assessed by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Western blotting was employed to analyze the impact on NF-κB signaling. In addition, MGP overexpression and p65 knockdown in HuCCT1 cells were co-transfected to study their combined effects on PD-L1 expression and CD8+ T-cell exhaustion markers. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were evaluated through colony formation assays and flow cytometry.
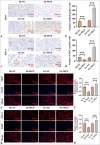
Results: Compared to adjacent tissues and human intrahepatic cholangiocellular epithelial cells, MGP was significantly overexpressed in ICC tumor tissues and HuCCT1 cells (P < 0.001). MGP overexpression led to NF-κB signaling phosphorylation (P < 0.001), elevated PD-L1 expression (P < 0.001), and heightened levels of CD8+ T-cell exhaustion markers (P < 0.001). Conversely, p65 knockdown mitigated the effects of MGP overexpression on HuCCT1 cell proliferation (P < 0.01) and CD8+ T-cell exhaustion (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001), while also significantly reducing PD-L1 expression (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: MGP promotes CD8+ T-cell exhaustion and facilitates immune evasion in ICC through NF-κB pathway activation.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; Immune escape; Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Matrix Gla protein; Programmed Death-Ligand 1.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
