Functional loss of rffG and rfbB, encoding dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase, alters colony morphology, cell shape, motility and virulence in Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 40469742
- PMCID: PMC12136496
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1572117
Functional loss of rffG and rfbB, encoding dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase, alters colony morphology, cell shape, motility and virulence in Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
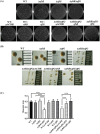
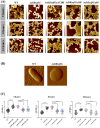
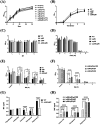
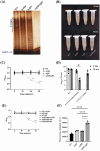
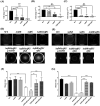
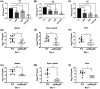
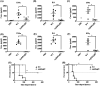
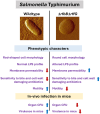
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) O-antigen and enterobacterial common antigen (ECA) play crucial roles in maintaining the outer membrane in Gram-negative bacteria. Mutations in the biosynthetic pathways of LPS and ECA may lead to accumulation of intermediates, resulting in morphological changes and activation of stress responses. However, the functional consequences of abrogation of both O-antigen and ECA synthesis in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) are not well investigated. In this study, we generated single and double-deletion mutants of rfbB and rffG, encoding dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase paralogs that are important in the synthesis of both O-antigen and ECA. Importantly, mutations in the dTDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydratase encoding gene in humans are known to cause Catel-Manzke syndrome, a rare genetic disease. All four strains, i.e., wild type (WT), ΔrfbB, ΔrffG and ΔrfbBΔrffG, grew well in rich Luria Bertani (LB) liquid media at 37°C; however, the functional loss of both rfbB and rffG, but not in single-deletion strains, resulted in round cell morphology and smaller colony size in LB agar plates. There was no significant differences in the growth of the four strains in minimal media at 37°C (nutritional deficiency), in LB at 42°C (high temperature), acidic pH or LB with 3-4% NaCl (high osmolarity; however the ΔrfbBΔrffG strain was hypersensitive to bile and cell wall-targeting antibiotics). These results demonstrated that the ΔrfbBΔrffG strain was sensitive to some stress conditions. Interestingly, the ΔrfbBΔrffG strain displayed an altered LPS profile, autoaggregated rapidly compared to the WT and the single mutant strains and showed high N-phenylnaphthylamine (NPN) fluorescence indicating greater surface hydrophobicity. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis identified flagellar and SPI-1 pathways to be highly downregulated in ΔrfbBΔrffG which led to impaired swimming as well as swarming motility, lower adhesion and invasion of HeLa cells. Importantly, the ΔrfbBΔrffG strain was less proficient in colonizing Peyer's patches, spleen and liver, was unable to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and was attenuated in both the oral and intraperitoneal models of S. Typhimurium infection in mice. Overall, this study highlights the importance of rfbB and rffG in maintaining cell wall and cell membrane integrity, colony and cellular morphology, motility and virulence in S. Typhimurium.
Keywords: 6-dehydratase; Salmonella Typhimurium; dTDP-D-glucose 4; enterobacterial common antigen; lipopolysaccharide; rfbB; rffG.
Copyright © 2025 Chakraborty, Banerjee, Joseph, Pathak, Verma, Karhale, Chandra, Das, Saha and Nandi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allard S. T. M., Giraud M.-F., Whitfield C., Graninger M., Messner P., Naismith J. H. (2001). The crystal structure of dTDP-d-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (RmlB) from Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium, the second enzyme in the dTDP-l-rhamnose pathway. J. Mol. Biol. 307, 283–295. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4470, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

