Efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization-hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with targeted therapy and immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
- PMID: 40469916
- PMCID: PMC12134975
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2025.15109
Efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization-hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with targeted therapy and immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis
Abstract
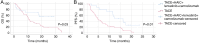
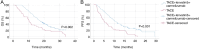
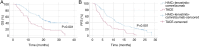
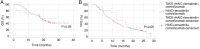
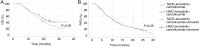
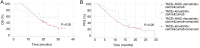
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) presents a notable therapeutic challenge. The efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) and systemic therapy using tyrosine kinase inhibitor and programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor has not been fully explored. In the present study, the clinical data from 251 patients with HCC and PVTT treated at Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (Harbin, China) between January 2021 and December 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were divided into four groups: TACE-HAIC + lenvatinib + camrelizumab (Group 1; n=16), TACE + lenvatinib + camrelizumab (Group 2; n=90), HAIC + lenvatinib + camrelizumab (Group 3; n=102) and TACE alone (Group 4; n=43). Clinical data included demographics, preoperative indices, tumor characteristics, medical history, performance status, liver function, pre-treatment α-fetoprotein levels and adverse events. Survival outcomes [overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS)] were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Group 1 exhibited significantly longer OS and PFS times compared with Group 4 (both P<0.05). Adverse events, including fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and immune-related pneumonitis, were more frequent in Group 1 (all P<0.001). Group 2 also showed improved OS and PFS times compared with Group 4 (both P<0.05), with notable differences in adverse event profiles. Group 3 demonstrated superior survival outcomes compared with Group 4 (P<0.05), although with a higher incidence of adverse events. No significant differences in OS or PFS times were observed between Groups 1 and 3, or between Groups 2 and 3, indicating comparable efficacy between TACE-HAIC + lenvatinib + camrelizumab and HAIC + lenvatinib + camrelizumab. In conclusion, TACE-HAIC combined with lenvatinib and camrelizumab significantly improved both OS and PFS times in patients with HCC and PVTT compared with TACE alone, despite a higher incidence of adverse events. This combination therapy represents a promising treatment strategy for this patient population, offering enhanced survival benefits.
Keywords: hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; overall survival; portal vein tumor thrombosis; progression-free survival; transarterial chemoembolization.
Copyright: © 2025 Hou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination Therapy of Chemoembolization and Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Compared with Chemoembolization Alone: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 14;2021:6670367. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670367. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34337041 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib plus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization with/without hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 7 cm with major portal vein tumor thrombosis: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Int J Surg. 2024 Dec 1;110(12):7860-7870. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001819. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38869974 Free PMC article.
-
The treatment of transarterial chemoembolization/hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitor is effective against hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A systematic review.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 9;13:1054072. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1054072. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36969065 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of HAIC (FOLFOX) combined with lenvatinib plus PD-1 inhibitors vs. TACE combined with lenvatinib plus PD-1 inhibitors in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus and arterioportal fistulas.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 15;13(11):5455-5465. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38058801 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of multimodality treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: patient-level network meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 16;14:1344798. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1344798. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38434681 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
