Localized exciton emission from monolayer WS2 nanoribbon at cryogenic temperature
- PMID: 40470086
- PMCID: PMC12133312
- DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2024-0583
Localized exciton emission from monolayer WS2 nanoribbon at cryogenic temperature
Abstract
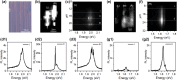
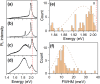
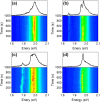
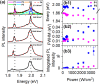
We conducted low-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy experiments on individual WS2 and MoSe2 nanoribbons prepared by gold-assisted exfoliation from the slanted surface of bulk crystals with a vicinal and stepwise pattern. The nanoribbons are predominantly monolayer and have widths varying from hundreds of nanometers down to tens of nanometers. Most MoSe2 NRs display an emission profile similar to 2D excitons of MoSe2 monolayers. In contrast, WS2 nanoribbons are characterized with sharp emission peaks that can be attributed to the emission from localized excitons or trions. Moreover a broad low energy emission peak can be also observed from some of the WS2 nanoribbons, which originates from bilayer regions. In this manuscript, we analyze spectral diffusion behavior along with pump power and temperature dependence of the localized exciton emission peaks, shedding light on potential of TMDC nanoribbons in sensing and opto-electronic applications.
Keywords: WS2 nanoribbon; localized exciton emission; low-temperature photoluminescence.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wang G., et al. Colloquium: excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides. Rev. Mod. Phys. . 2018;90(2):021001. doi: 10.1103/revmodphys.90.021001. - DOI
-
- Xu X., Yao W., Xiao D., Heinz T. F. Spin and pseudospins in layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Phys. . 2014;10(5):343–350. doi: 10.1038/nphys2942. - DOI
-
- Yu H., Cui X., Xu X., Yao W. Valley excitons in two-dimensional semiconductors. Natl. Sci. Rev. . 2015;2(1):57–70. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwu078. - DOI
-
- Atatüre M., Englund D., Vamivakas N., Lee S., Wrachtrup J. Material platforms for spin based photonic quantum technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. . 2018;3(5):38–51. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0008-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
