Electro-optic frequency shift of single photons from a quantum dot
- PMID: 40470089
- PMCID: PMC12133247
- DOI: 10.1515/nanoph-2024-0550
Electro-optic frequency shift of single photons from a quantum dot
Abstract
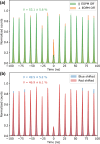
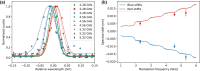
Quantum dots (QDs) are a promising source of single photons mainly due to their on-demand operation. However, their emission wavelength depends on their size and immediate surroundings in the solid-state environment. By applying a serrodyne electro-optic phase modulation, we achieve a spectral shift up to 0.01 nm (3.5 GHz) while preserving the purity and indistinguishability of the photons. This method provides an efficient and scalable approach for tuning the emission wavelength of QDs without relying on nonlinear frequency mixing or probabilistic processes. Our results show that the electro-optic phase modulation enables stable and tunable spectral shifts, making it suitable for applications such as quantum communication, quantum key distribution, and primarily integrating remote quantum dot sources into large-scale quantum networks.
Keywords: electro-optic phase modulation; quantum dots; quantum interface; quantum photonics; single-photon source; spectral shift.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tichy M. C. Interference of identical particles from entanglement to boson-sampling. J. Phys. B: At., Mol. Opt. Phys. . 2014;47(10):20240550. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/47/10/103001. Art. no. 103001. - DOI
-
- Münzberg J., et al. Symmetry allows for distinguishability in totally destructive many-particle interference. PRX Quantum . 2(6):20240550. doi: 10.1103/prxquantum.2.020326. 2021, Art. no. 020326. - DOI
-
- Wang H., et al. High-efficiency multiphoton boson sampling. Nat. Photonics . 2017;11(6):361–365. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2017.63. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
