Diffusion of DNA on Atomically Flat 2D Material Surfaces
- PMID: 40471129
- PMCID: PMC12177950
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c16277
Diffusion of DNA on Atomically Flat 2D Material Surfaces
Abstract
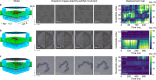
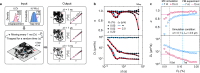
Accurate localization and delivery of biomolecules are pivotal for building tools to understand biology. The interactions of biomolecules with atomically flat 2D surfaces offer a means to realize both the localization and delivery, yet experimental utilization of such interactions has remained elusive. By combining single-molecule detection methods with computational approaches, we comprehensively characterize the interactions of individual DNA molecules with hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) surfaces. Our experiments directly show that, upon binding to a hBN surface, a DNA molecule retains its ability to diffuse along the surface. Further, we show that the magnitude and direction of such diffusion can be controlled by the DNA length, the surface topography, and atomic defects. We observe that the diffusion speed of the biomolecules is significantly lower than indicated by molecular dynamic simulations. Through computational analysis, we present the model based on temporary trapping by atomic defects that accounts for those observations. By fabricating a narrow hBN ribbon structure, we achieve pseudo-1D confinement, demonstrating its potential for nanofluidic guiding of biomolecules.
Keywords: DNA; hexagonal boron nitride; nanofluidics; surface diffusion; van der Waals materials.
Figures



References
-
- Yusko E. C., Bruhn B. R., Eggenberger O. M., Houghtaling J., Rollings R. C., Walsh N. C., Nandivada S., Pindrus M., Hall A. R., Sept D., Li J., Kalonia D. S., Mayer M.. Real-Time Shape Approximation and Fingerprinting of Single Proteins Using a Nanopore. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017;12(4):360–367. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2016.267. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

