IDO2-AhR axis as central regulator of the kynurenine pathway in glioblastoma
- PMID: 40471422
- PMCID: PMC12263720
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-025-05106-w
IDO2-AhR axis as central regulator of the kynurenine pathway in glioblastoma
Abstract
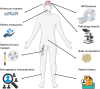
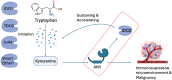
Purpose: Upregulation of the Kynurenine Pathway (KP) in Glioblastoma (GBM) plays an important role in driving its treatment-resistant immunosuppressive microenvironment. Factors driving this exaggerated pathway remain poorly understood. Our aim was to explore the correlation between key KP markers; IDO1, IDO2, TDO2, its primary effector target aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and a comprehensive set of clinical- and tumour characteristics.
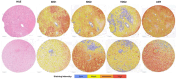
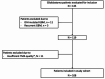
Methods: Tissue samples from 108 newly diagnosed GBM patients were analyzed for the expression of TDO2, IDO1, IDO2, and AhR using immunohistochemistry and QuPath software. Exploratory analyses were conducted to evaluate correlations between KP marker expression and clinical, radiological, and molecular data.
Results: IDO1 expression was primarily correlated with inflammatory blood markers, while TDO2 was correlated with patient age, gender, smoking habit and medication use. In contrast, AhR and IDO2 demonstrated hardly any correlations with clinical or tumour characteristics. Notably, IDO2 exhibited a strong association with AhR expression and tumour cell density, with no observed correlation between AhR and either IDO1 or TDO2.
Conclusions: We validated the inflammatory influences on IDO1 expression and found that TDO2 was mostly correlated with medication and patient characteristics. We could not confirm IDO1 and TDO2 as most prominent drivers of AhR activity in the KP. However, we found a strong correlation between IDO2-AhR which may be responsible for the sustained and enhanced immunosuppression within the tumour microenvironment. This could explain recent failures of IDO1 and TDO2 antagonists and might redirect future studies to intervene in the kynurenine-AhR-IDO2 axis.
Keywords: AhR; Glioblastoma; IDO; Kynurenine; TDO2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Delgado-López PD, Corrales-García EM (2016) Survival in glioblastoma: a review on the impact of treatment modalities. Clin Transl Oncol 18:1062–1071. 10.1007/s12094-016-1497-x - PubMed
-
- Bao Z, Wang Y, Wang Q, Fang S, Shan X, Wang J, Jiang T (2021) Intratumor heterogeneity, microenvironment, and mechanisms of drug resistance in glioma recurrence and evolution. Front Med 15:551–561. 10.1007/s11684-020-0760-2 - PubMed
-
- Sordillo PP, Sordillo LA, Helson L (2017) The kynurenine pathway: A primary resistance mechanism in patients with glioblastoma. Anticancer Res 37:2159–2171. 10.21873/anticanres.11551 - PubMed
-
- Vázquez Cervantes GI, Arellano N, Ortega D, Salazar A, González-Esquivel D, Rios C, Pineda B, Cruz V (2017) Role of Kynurenine Pathway in Glioblastoma
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

