miR-210 Regulates Autophagy Through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Reduces Neuronal Cell Death and Inflammatory Responses, and Enhances Functional Recovery Following Cerebral Hemorrhage in Mice
- PMID: 40471451
- PMCID: PMC12141382
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-025-04434-7
miR-210 Regulates Autophagy Through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Reduces Neuronal Cell Death and Inflammatory Responses, and Enhances Functional Recovery Following Cerebral Hemorrhage in Mice
Abstract
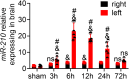
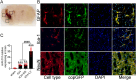
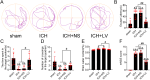
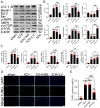
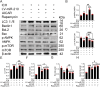
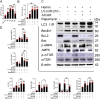
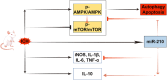
Recently, a growing body of research has shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) are crucial in the pathophysiological mechanisms of brain disorders, miR-210 is one of the significant miRNAs implicated in these disorders, and its function in intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is not yet fully understood. Research the impact of miR-210 on intracerebral hemorrhage and probe into its working mechanism. The ICH model was established by injecting collagenase into the basal ganglia of male C57/BL6 mice (n = 142). Firstly, the mice were divided into sham group (n = 6) and ICH group (n = 30) (3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h), the samples of the sham group were collected at 48 h after operation, the brain tissues of the left and right basal ganglia were collected in each groupand. qPCR was used to detect the level of miR-210 in each group. Then, LV-miR-210 was injected into the lateral ventricle to establish a model of miR-210 overexpression, and NS injection was set as a comparison, which was divided into sham group (n = 15), ICH group (n = 15), ICH + NS group (n = 15), and ICH + LV-miR-210 group (n = 15). Water maze training was started on the 2 d after surgery. qPCR was used to detect the levels of miR-210, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 in each group at 3 d after operation. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of p-AMPK/AMPK, p-mTOR/mTOR, Beclin 1, Bax, Bcl-2, and LC3 II/I in each group. Immunofluorescence was used to detect the expression of lentivirus-mediated miR-210 in mouse brain. Water maze was used to evaluate the learning and memory function of the mice. The dry-wet method was used to evaluate brain edema, TUNEL was used to detect the apoptosis of brain cells in each group. Then, Rapamycin and AICAR were used to intervene p-AMPK/AMPK and p-mTOR/mTOR, and they were divided into sham group (n = 6), ICH group (n = 6), ICH + LV-miR-210 group (n = 6), ICH + LV-miR-210 + AICAR group (n = 6), and ICH + LV-miR-210 + Rapamycin group (n = 6). The levels of miR-210 in each group were detected by qPCR at 3 d after operation, and the levels of p-AMPK/AMPK, p-mTOR/mTOR, Beclin 1, Bax, Bcl-2, and LC3 II/I in each group were detected by WB. Finally, HT22 cells were stimulated with Hemin to construct an in vitro intracerebral hemorrhage model, and the time gradient was set (control group, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h). qPCR was used to detect the expression of miR-210 in each group. Then HT22 cells were transfected with lentivirus, and rapamycin and AICAR were used to interfere with p-AMPK/AMPK and p-mTOR/mTOR. Control group, Hemin group, Hemin + LV-miR-210 group, Hemin + LV-miR-210 + AICAR group, and Hemin + LV-miR-210 + Rapamycin group. qPCR was used to detect the level of miR-210 in each group. The levels of p-AMPK/AMPK, p-mTOR/mTOR, Beclin 1, Bax, Bcl-2, and LC3 II/I in each group were detected by Western blotting. miR-210 is significantly increased in a short time after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. miR-210 can alleviate secondary injury of ICH by improving neurological deficit and reducing brain edema. In addition, upregulation of miR-210 expression inhibited autophagy and alleviated apoptosis and inflammation. In our study, we found that miR-210 significantly inhibited the activation of AMPK/ mTOR pathway triggered by ICH, and the neuroprotective effect of miR-210 was partially reversed when Rapamycin and AICAR reversed this inhibition. At the mechanistic level, miR-210 exerts its function by regulating AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting autophagy and reducing apoptosis and inflammation. Further studies at the cellular level were basically consistent with the above results. miR-210 is up-regulated after ICH and can play a neuroprotective role by regulating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway mediated by autophagy, suggesting that it may become a therapeutic target for reducing nerve injury after ICH.
Keywords: miR-210; Apoptosis; Autophagy; Cerebral hemorrhage; Neuroinflammation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: The protocol for animal experimentation was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Nantong University Laboratory Animal Center. The study results are reported adhering to ARRIVE guidelines, and the protocol number is (S20220221-035). Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Galactin-8 DNA methylation mediates macrophage autophagy through the MAPK/mTOR pathway to alleviate atherosclerosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):603. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-85036-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747459 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the underlying mechanisms of "Xingnao Kaiqiao" acupuncture for cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury based on AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jul 25;50(7):782-789. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240384. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40691028 Chinese.
-
[6-Shogaol alleviates cerebral injury after cardiac arrest-cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats by inhibiting death-associated protein kinase 1-mediated autophagy].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Jun;37(6):568-575. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240724-00627. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40820533 Chinese.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
Cited by
-
NSC-derived extracellular vesicles-mediates neuronal plasticity enhancement in vascular dementia via transferring miR-210.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Jul 9;13(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02073-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40635095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li X, Feng D, Chen G (2018) An update on medical treatment for intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res Published Online September 11. 10.1007/s12975-018-0664-5 - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Anne Stetler R, Yang QW (2014) Inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: from mechanisms to clinical translation. Prog Neurobiol 115:25–44. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.003 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SJCX24_2069/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- 2022JY003/the General program of clinical basic Research in Nantong University
- KD2022KYCXTD006/The first phase of "Research Innovation Team Project" of Kangda College of Nanjing Medical University
- KF2203-93/National Key Laboratory of Oncology System Medicine Open Fund
- 82074524/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- MS2023073,MS2022014/Project of Nantong Health Commission
- 2022LY009/Clinical Research Program of Nantong University
- 2022HY003/Nursing Research Program of Nantong University
- MS2021060/Jiangsu Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Program Project
- MSZ2023156/Nantong science and technology project
- KD2023KYJJ269/Research Project of Kangda College, Nanjing Medical University
- 2023HY001/Nantong university 2023 clinical medicine special project
- Z2022067/Guiding Project of Health Commission of Jiangsu Province
- KD2022JYYJZD005/Educational Research Project of Kanda College of Nanjing Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

