Intratumoral and peritumoral ultrasound radiomics analysis for predicting HER2-low expression in HER2-negative breast cancer patients: a retrospective analysis of dual-central study
- PMID: 40471472
- PMCID: PMC12141173
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02752-4
Intratumoral and peritumoral ultrasound radiomics analysis for predicting HER2-low expression in HER2-negative breast cancer patients: a retrospective analysis of dual-central study
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to explore whether intratumoral and peritumoral ultrasound radiomics of ultrasound images can predict the low expression status of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in HER2-negative breast cancer patients.
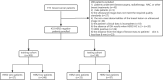
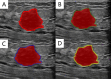
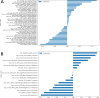
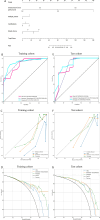
Methods: HER2-negative breast cancer patients were recruited retrospectively and randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 303) and a test cohort (n = 130) at a ratio of 7:3. The region of interest within the breast ultrasound image was designated as the intratumoral region, and expansions of 3 mm, 5 mm, and 8 mm from this region were considered as the peritumoral regions for the extraction of ultrasound radiomic features. Feature extraction and selection were performed, and radiomics scores (Rad-score) were obtained in four ultrasound radiomics scenarios: intratumoral only, intratumoral + peritumoral 3 mm, intratumoral + peritumoral 5 mm, and intratumoral + peritumoral 8 mm. An optimal combined nomogram radiomic model incorporating clinical features was established and validated. Subsequently, the diagnostic performance of the radiomic models was evaluated.
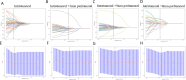
Results: The results indicated that the intratumoral + peritumoral (5 mm) ultrasound radiomics exhibited the excellent diagnostic performance in evaluated the HER2 low expression. The nomogram combining intratumoral + peritumoral (5 mm) and clinical features showed superior diagnostic performance, achieving an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.911 and 0.869 in the training and test cohorts, respectively.
Conclusion: The combination of intratumoral + peritumoral (5 mm) ultrasound radiomics and clinical features possesses the capability to accurately predict the low-expression status of HER2 in HER2-negative breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Breast cancer; HER2 status; Radiomics scores; Ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the hospital and obtained ethics approval in written (SL-YX2022-015). Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Llombart-Cussac A, Cortés J, Paré L, Galván P, Bermejo B, Martínez N, et al. HER2-enriched subtype as a predictor of pathological complete response following trastuzumab and lapatinib without chemotherapy in early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer (PAMELA): an open-label, single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:545–54. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30021-9. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
