Temporal Trends of Hospital Admissions Due to Heart Failure in Brazil
- PMID: 40471566
- PMCID: PMC12133065
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20240505
Temporal Trends of Hospital Admissions Due to Heart Failure in Brazil
Abstract
Background: Heart failure is a global pandemic that causes a significant reduction in quality of life, with an impact on hospital expenses. It is important to know the temporal trends of hospitalizations and mortality in order to outline coping strategies.
Objective: The objective of this study was to describe the temporal trends of hospitalizations due to heart failure and mortality during hospitalizations between 2000 and 2021 in Brazil.
Methods: We conducted a study on temporal trends in the rates of hospitalization and mortality during hospitalization, using data from the Department of Information Technology of the Brazilian Unified Health System, by means of joinpoint regression. We calculated the annual percentage change of the rates with respective 95% confidence intervals and alpha significance level of 0.05.
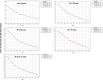
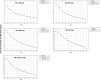
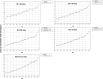
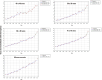
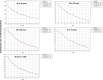
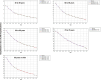
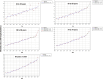
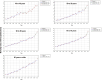
Results: We analyzed 2,851,437 hospitalizations in men and 2,749,424 hospitalizations in women between 2000 and 2021 in Brazil. Regarding hospitalization rates, there was an annual percentage decrease of 6.7% to 8.1% in men and a decrease of 7.5% to 8.3% in women. With respect to mortality rates, there was an annual percentage increase of 1.8% to 3.6% in men and an increase of 3.1% to 3.5% in women.
Conclusion: We observed a decrease in the rates of hospitalization due to heart failure and an increase in the mortality rates in all age ranges assessed, in both sexes, between 2000 and 2021 in Brazil. These findings may reflect better disease control and hospitalization only for more severe cases, but we emphasize the need for continued management of risk factors for the disease.
Fundamento: A insuficiência cardíaca é uma pandemia global e causa de redução significativa da qualidade de vida, com impacto nos gastos hospitalares, sendo importante conhecer a tendência temporal das internações e mortalidade para traçar estratégias de enfrentamento.
Objetivo: O objetivo deste estudo foi descrever a tendência temporal das internações hospitalares por insuficiência cardíaca e mortalidade durante as internações entre 2000 e 2021 no Brasil.
Métodos: Foi realizado estudo de tendência temporal das taxas de internação e mortalidade durante internações, utilizando-se dados do Departamento de Informática do Sistema Único de Saúde, por meio de regressão segmentada joinpoint. Foram calculadas as variações percentuais anuais das taxas com os respectivos intervalos de confiança de 95% e nível alfa de significância de 0,05.
Resultados: Foram analisadas 2.851.437 internações em homens e 2.749.424 em mulheres entre 2000 e 2021 no Brasil. Observou-se redução percentual anual das taxas de internação em homens de 6,7% a 8,1% e, em mulheres, redução de 7,5% a 8,3%. Observou-se aumento percentual anual das taxas de mortalidade em homens de 1,8% a 3,6% e, em mulheres, aumento de 3,1% a 3,5%.
Conclusão: Observou-se redução das taxas de internação por insuficiência cardíaca e aumento das taxas de mortalidade em todas as faixas etárias avaliadas para ambos os sexos entre 2000 e 2021 no Brasil. Estes resultados podem refletir melhor controle ambulatorial da doença e internação apenas para casos mais graves, mas ressaltamos a necessidade de abordagem continuada dos fatores de risco para a doença.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation . 2022;145(18):895–1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

